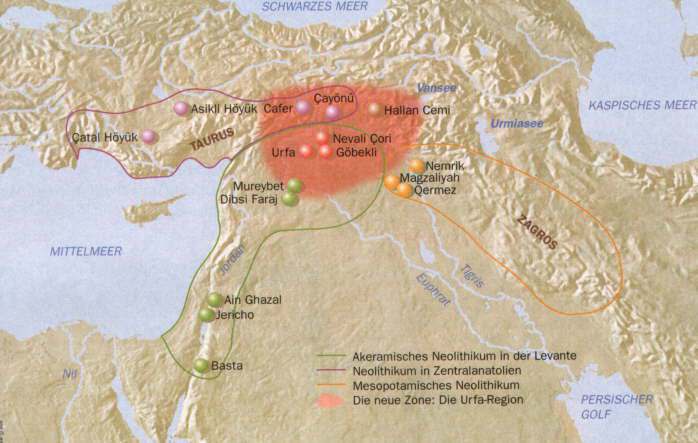
The origins of farming
G-M201
The haplogroup G distibution

The origins of farming |
G-M201 |

The haplogroup G distibution |
|
* |
|
* The OriginY-DNA Haplogroup G-M201 stems from GHIJK-F1329, is formed in west Asia about 50,000 ybp and split in two subgroups G1-M342/M285 and G2-P287 about 25,000 ybp. At present G is a small haplogroup in Europe with an occurrence from 3% to 7%, somewhat more at places in the Alps, and increasing to 10% on the islands of Sardinia and Corsica. Haplogroup G seems to have had a slow start, evolving somewhere in West Asia in isolation for tens of thousands of years, G did not participate in the earlier colonization of Eurasia. (1) Now about 2,5 % of the World population has this haplogroup. (2) G1-M342/M285 and G2-P287 entered Europe in Neolithic times in several waves, together with J1 and/or J2. It has subsequently declined in number, and was minimized upon the arrival in Europe of the corded ware culture in the Iron Age. It is often found in European archaeological DNA. 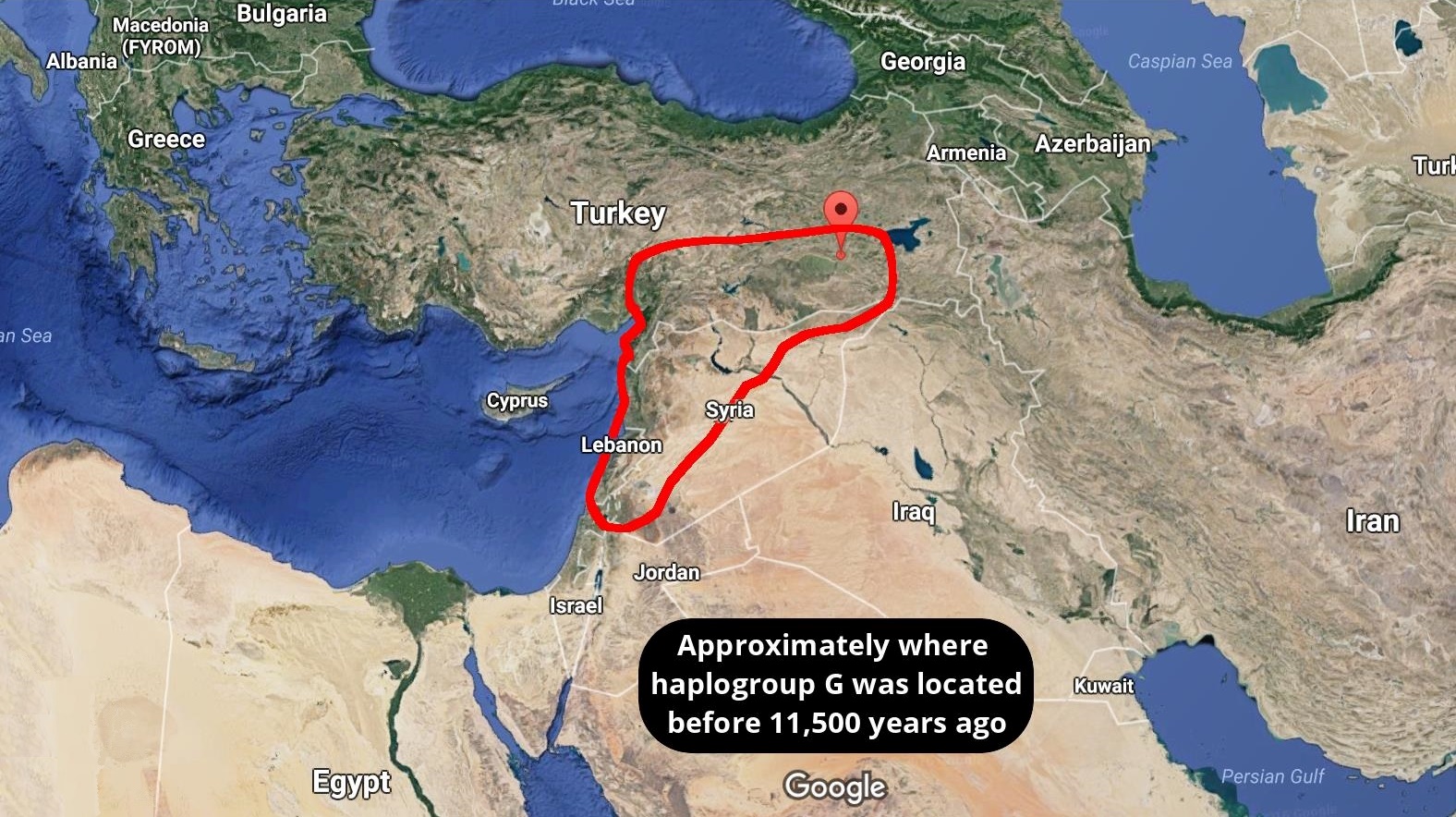
Haplogroup G first locations (T. Kandell). |
|
The most probably region of the initial phase of G-M201 is estimated to be in Anatolia, Armenia or western Iran. For this are several indications. First, here is the only region with co-presence of deep basal branches as well as the occurrence of high sub-haplogroup diversity of haplogroup G. This map on the right side of Europe and Asia Minor shows the probable area of the beginning time of Haplogroup G in green. The decreasing spread of this group is indicated by fading from a dark to lighter green, to yellow and then to brown. (3) |
|
|
Furthermore there is the similarity between the mtDNA haplogroups found in archaeological remains of the first European immigrants after the Ice Ages and the archaeological mtDNA found in Anatolia. They have the highest resemblance of mtDNA in the world. In various regions of the Near East, the so called Fertile Crescent, lived hunter-gatherers. The two best known groups are the the Baradostian, 34,000 – 20,000 ybp of the Zagros Mountains of western Iran and the Levanto-Aurignacian, 27,000 – 20,000 ybp in the Levant. These hunters were evidently migratory throughout the territories they occupied; of permanent occupation there is no trace. Here lived Our G forefather and his descendants only split round 27,000 ybp in two subgroups. G1-M342/M285 probably on the east side of the community, G2-P287 in the central and western part. G2a-P15 came again much later. It was formed 20700 ybp and had a TMRCA of 18000 ybp. Slowly they grew in the Fertile Crescent region as a proto-agrarian semi-sedentary hunter gatherers society. First in the warm and moist Bølling-Allerød interstadial, 14,700 to 12,700 ybp there was a rapid population growth in G and as a result emerged many subgroups. They lived in a population with Pre-Pottery Neolithic Culture which existed there for about 4 millennia. Pre Pottery Neolitic (11,700-8,800) ybpPrior evidence based on ice cores taken from Greenland has suggested that a strike by a comet may have led to the onset of the Younger Dryas a period of Earth cooling that lasted for approximately 1000 years. Other evidence also suggests that the cooling period caused groups of people to band together to cultivate crops, leading to the development of agriculture, which in turn led to huge leaps in technological innovations and societal developments, i.e. Neolithic civilization. In this new effort, the researchers describe evidence they found on a stone pillar at Gobekli Tepe (the oldest known temple site) that aligns with the ice core findingsthat a comet struck the Earth in approximately 10,950BC. Around 12,000-11,000 ybp, humans began practicing agriculture here and started making pottery. The first urban society began in Göbekli Tepe around 11,550 ybp (9,500 BC). Probably this was a special place of worship. They built here their first temples and homes. 
The origins of farming in Anatolia and the fertile crescent. (4) At the end of this youngest Dryas period, that lasted about a thousand years, the old knowledge remained preserved and was passed on. The cornfields were operated again by the Natufians as at Jericho and Abu Hureyra. The population concentration was larger now than ever with up to 500 inhabitants. In the fertile Peninsula, a remarkable amount of cultural diversity soon emerged. Grain silos and a wall were built around the Jericho of that time.Jericho would then be the oldest city in the world. |
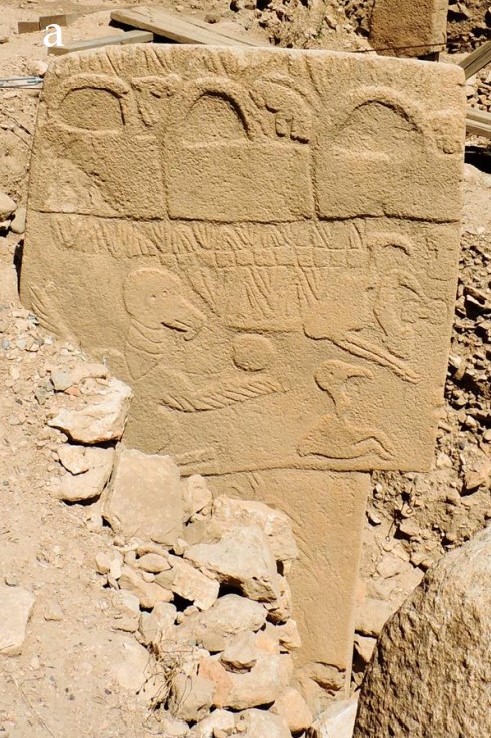

Vulture Stone of Göbekli Tepe |
Much of the symbolism of Göbekli Tepe is interpreted in terms of astronomical events. By matching low-relief carvings on some of the pillars at Göbekli Tepe to star asterisms has been found compelling evidence that the famous Vulture Stone is a date stamp for 10950 BC ± 250 yrs, which corresponds closely to the proposed Younger Dryas event, estimated at 10890 BC. Evidence is found that a key function of Göbekli Tepe was to observe meteor showers and record cometary encounters. Indeed, the people of Göbekli Tepe appear to have had a special interest in the Taurid meteor stream, the same meteor stream that is proposed as responsible for the Younger-Dryas event. Doing so revealed associations between characters on the pillar and astronomical symbols in the sky for the year 10,950 BC. The fact that the people took the time and considerable effort to create the characters on the pillar suggests something very important must have happened during the same time period that the Greenland ice core suggests a comet struck, approximately 12,900 ybp. |

Wall pillars with three animal symbols in series. Wall pillars with three animal symbols The researchers have concluded that the carvings on the pillar were likely meant to document the cataclysmic event and suggest that the temple may have been an observatory. (4a) Around 10.000 ybp the earliest archaeo-botanical remains of long-term plant management in the world appears in the Fertile Crescent. It is a domesticated-type "Emmer wheat". * The archaeo-botanical remains from Boncuklu Höyük in west Anatolia to Çatal Höyük in south Anatolia in Türkiye and Chogha Golan in the Zagros mountains in West Iran represent the earliest records of long-term plant management. In the north of the Fertile Crescent, between 10,500 and 9,500 ybp began the domestication of the four later farm animals: sheep, goat, pig and cattle. The Proto-Neolithic site of Zawi Chemi Shanidar in Irac dated from the 11th millennium BC to the 9th millennium BC is one of the first semi-permanent sedentary communities in human history. In the middle of the rocky terrain of the Zagros Mountains in Northern Iraq, where a branch of the Tigris River created fertile plains. on the left bank of the Greater Zab River that allowed for the Proto-Neolithic people to cobble together a stable and sustainable subsistence economy based on a broad array of collected plants including wild cereals and grasses as well as fruits and nuts. Zawi Chemi residents also hunted and collected a wide range of different animal species that included wild sheep and goats, wild boar, various species of birds, and thousands of land snails. It is an early human civilization during the transition from nomadic lifestyles to sedentary settlements that points to the later practice of domestication of animals and plants. (5) * Pottery Neolitic (6,800 BCE)
"Seated Goddess" figurines from the Halaf Culture c. 5,500 BCE, Tepecik-Ciftlik before 6,500 BCE, and Çatalhöyük c. 7,000 BCE. The first pottery is found in Anatolia at Çatal höyük dated Çatal Höyük gives a detailed picture of the changes that occur over time. Prior to 6,500 BCE there are serried built-up areas, which are seen as a high degree of cohesion, but after that the structure differs into a large number of smaller units, separated by open spaces, indicating a shift from collectivity to individual households. At the same time, the number of inhabitants decreases in the old settlement, while flat new settlements are established. In the Levant the same thing happened a few centuries earlier. This change is related to the emergence of an intensive mixed farm company, which was created by combining arable farming and livestock farming. As a consequence, revenues increased and the population grew, increasing space for each household. Enterprising children moved to new settlements. 
Mount Hasan where the G-PF3147 people of Tepecik-Çiftlik got their obsidian * ARCHAEOGENETICSPalegawra cave, Iraqi KurdistanThe oldest archaeologically G is found in the Zawi Chemi layer B of the Shanidar Cave in the Zagros Mountains in Iraqi Kurdistan. This is G2a1-Z6552*, dated 12.815 ybp, 13.101-12.429 cal. BCE. (7a) 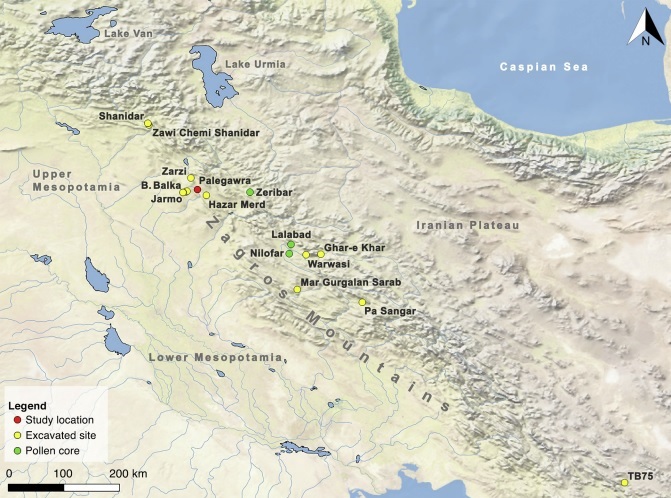
The location of sites mentioned in The Zagros Epipalaeolithic revisited, Eleni Asouti e.a.
* Boncuklu, Anatolia, TürkyeMillennia later in Boncuklu Höyük, the site of a 10,500 year old village near the City of Konya in the high Anatolian plateau of Central Türkiye three samples are found of G2a2b2b2-PH488, dated 8300-7950 BCE. (7) |
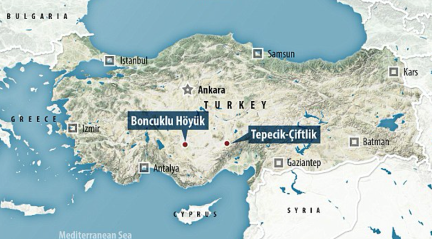
Anatolia |

Tepecik-Ciftlik-tatarliziyaret |
|
In Çatalhöyük in South Anatolia, is the oldest archaeological find of G2a2a1a3a-BY133179, dated about 68256635 BCE. Çatalhöyük was first settled around 7100 BCE and there lived more than 10,000 people. G2a2a1a3a-BY133179 formed 8.500 BCE has archaeological finds in Çatalhöyük 6900 BCE, Starçevo 5.500 BCE, Spain 5140 BCE, Serbia 4500 BCE, Croatia 4200 BCE, Ukraine 4700 BCE, Czech rep. 4600 BCE and Portugal 3000 BCE. Nowadays in people in UK. (8) The next archaelogical comes from at Tepecik Ciftlik. This was a G2a2a2-Z36520 dated to 6635-6475 cal BCE. The oldest G2b comes from the Wezmeh Cave in the Zagros Mountains, the far west of Iran. Here lived a man 7,250 BCE. He most likely had brown eyes, relatively light skin, and black hair, although Neolithic Iranians carried reduced pigmentation-associated alleles in several genes, showing the strongest signatures of selection in ancient Eurasians. (9) 
Excavations in Çatalhöyük, Türkiye (10) * Leaving the Region
It has been suggested that leaving the settlements in Anatolia was the result of a climate change that had the multiple negative consequences. First, there was global warming after the last ice age that led to a significant rise in sea level, pushing coastal inhabitants inland. This was exacerbated by the associated breakthrough of the Bosphorus, which greatly increased the level of the Black Sea, where many coastal inhabitants were also driven inland. 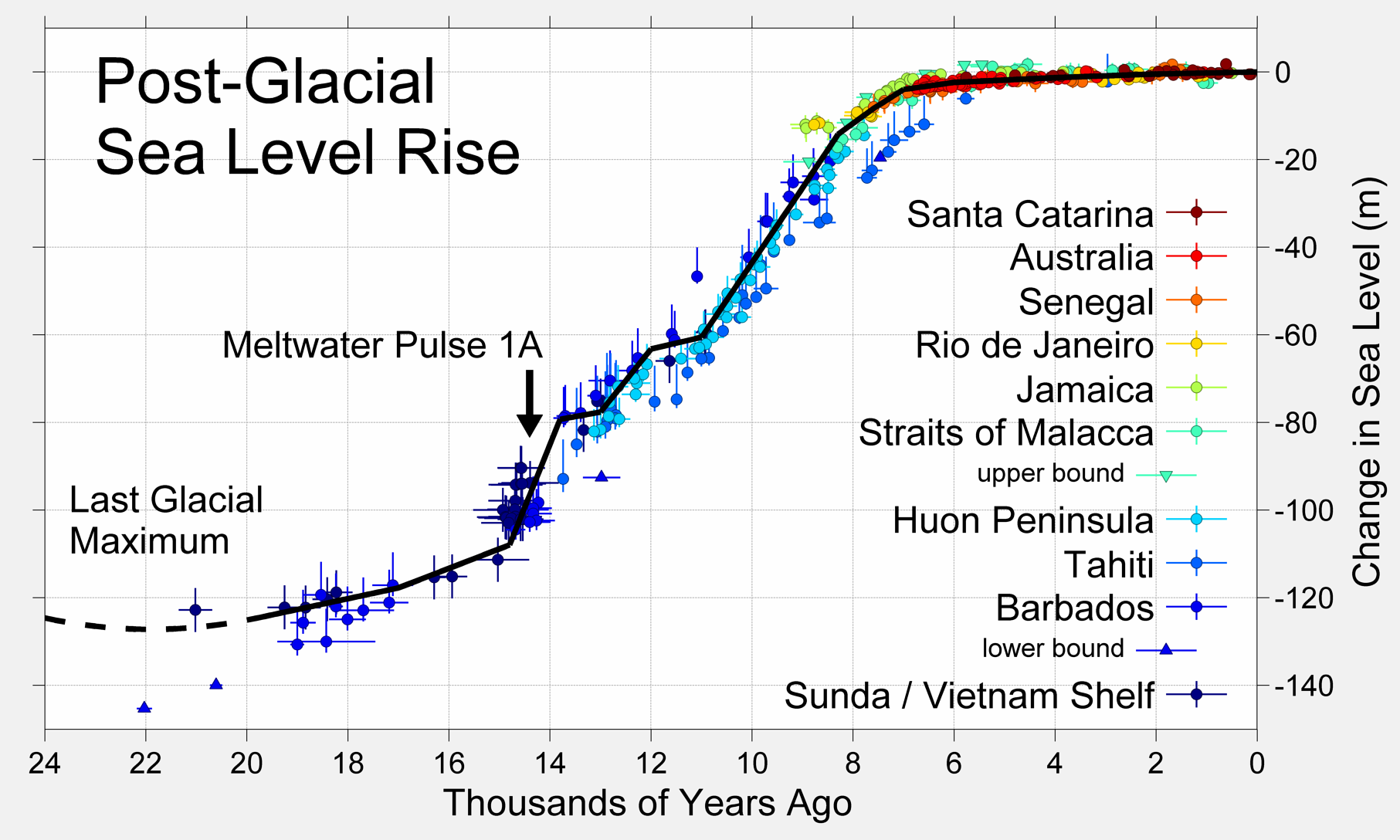
Post glacial sea level rise (6) There was also the the Misox oscillation. For three centuries the region became hotter and drier. Agriculture and livestock declined and as a result the yields of agriculture decreased. The G population left the region and migrated in all directions, The most western groups went westward to Europe, the eastern groups in the Zagros went eastward to central and southern Asia and northward to the Caucasus and the Russian steppes, southward to the Arabian peninsula and back to Africa to Egypt and Libya and probably already then to Morocco and took with them seed and their livestock. G1 which probably lived somewhat separated apart moved eastward to the Indus and from there North to Kazakhstan. The G2a1 groups went to the Caucasus. The G2a2 and subgroups spread westward to Türkiye and Europe, G2b went eastward to central and southern Asia. The beginning of expansion to Europe was already before 8500 BP to three regions in west Anatolia: the lake area near Antalya, the coasts on both sides of the Aegean sea, and in the Northwest of Anatolia around the Marmara Sea at Barcin Höyük. In these regions the G2a2a and the G2a2b groups lived still together and from here they entered Europe about 6000 BCE and they did that through two different routes, one by sea, the Mediterranean group and one across the country, the continental group. 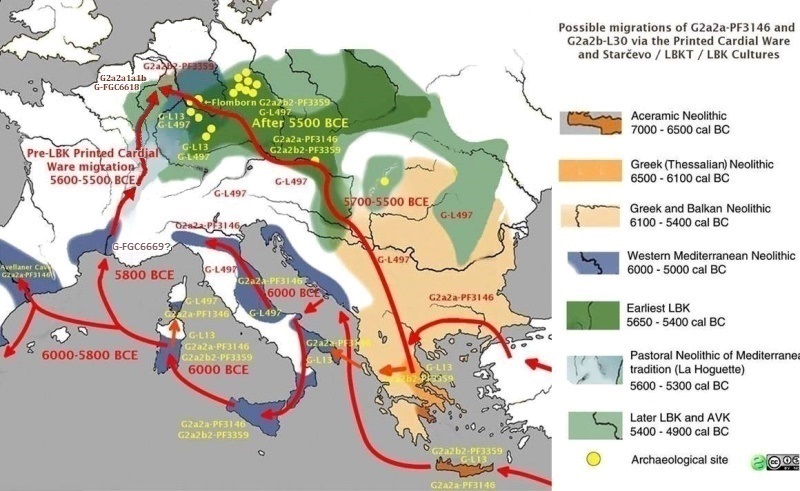
Possible migrations Routes of G2a2a-PF3147 and G2a2b-l30.
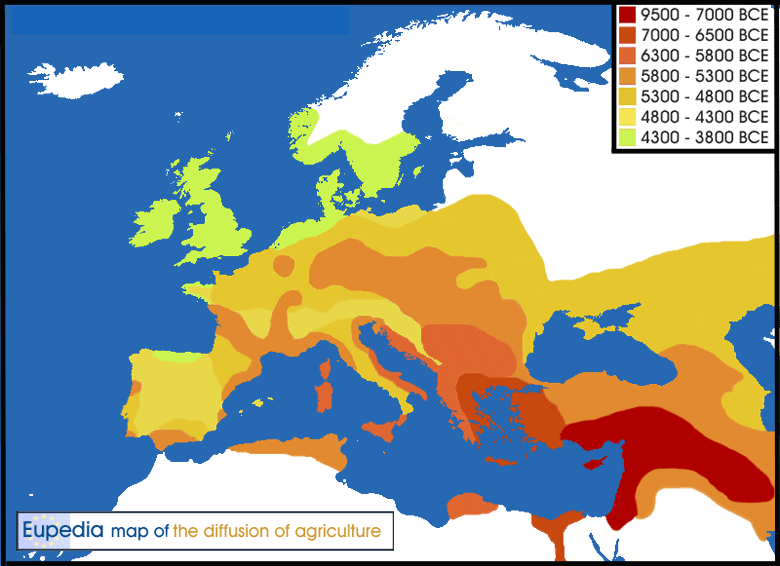
Diffusion of farming through Europa. The Hesbaye is the round area beneath Holland, tinted in the color of 5800 - 5300 years BCE. * A. The Continental groupThe very earliest Neolithic Farmers got to Europe at Revenia in Greece around 6,600 BCE. They went through Macedonia to Serbia and Bulgaria through the valleys of the Morava and Danube to Hungary. They reach the Hungarian plain about 5,800 BCE. Here are many archaeological finds of them, they continue along the Danube and the Rhine to Western Europe. They reached Germany around 5,500 BCE and Belgium and the North of France 5,200 BCE. By the characteristic decorations of their pottery this is called the Linear Band Culture, LBK. The majority of the Early Neolithic Farmers in central Europe was a mixture of G2a2a-PF3147 and G2a2b-l30. This is found in a number of consecutive Neolithic cultures, the Linearbandkeramik (LBK), flourishing about 5500-4500 BCE in Germany and Italy, the Rössen Culture (RSC) flourishing about 4,400-4250 BCE, Bell Beaker culture (D: Glockenbecher-Kultur) flourishing in Europe and England from between 2850 and 2140 BCE. This remained common in many places down to the start of the Early Bronze Age around 3200 BCE when we find Ötzi and the many G2a's from Treilles in Aveyron, in Southern France. In Southern Limburg, the Hesbaye and Condroz, the LBK culture flourishes from 5,500 BCE. They meet the Hoguettians here. Through Lorraine, a branch went through the basin of Paris to the Channel and Hainaut. 
Reconstruction of an LBK village at the Cannerberg near Maastricht dated ca 7,300 years ago. (6a) There has been a rapid population growth with a growth of 25% per generation. In South Limburg lived in the heyday up to 2000 people. This is as much as the Mesolithic population of the whole of the Netherlands. At the beginning of the Iron Age, around 2,500 BC the existing population in Europe is replaced by a people originating from the Russian steppes. Their males were carriers of haplogroup R. Carriers of haplogroup G2a2a then disappear. B. The Maritime groupFrom the coatst of the Aegean Sea they went to the Levant to Cyprus and Crete. They are the carriers of the Cardial ware culture They reach in 8,200 BP Italy and then approximately 5,500 BCE the Spanish and North African coast, Later Portugal is reached along the Spanish coasts. Not only the coasts of the country were colonized but also the islands, such as Corsica and Sardinia, and the interior to the Italian Alps A part goes in France north along the Rhône and Loire to the Atlantic coast. Their characteristic pottery found in Normandy near La Hoguette. These Hoguettians are also found across the Rhine at Stuttgart and Worms. They were also in South Limburg where they lived next to the continental LBK branch. They may have arrived at the same time. It is very likely that many of these have taken the crossing to Britain, included Ireland. They will have taken the shortest crossing near Calais. The British Neolithic farmers were genetically comparable to contemporary populations in continental Europe, and especially to the Neolithic Iberians, residents of the Spanish east coast, suggesting that some of the peasant families in Britain came along the Mediterranean and not the continental way along the Danube. * G2a people may have been the first modern humans who had acquired the alleles for fair skin. This is seen in an Early Neolithic farmer from Germany who possessed the same alleles for fair skin as the modern Europeans nowadays, while in an archaeologic found of a G2b man in the from Wezmeh Cave in Zagros, Iran, who was from ± 7,250 BCE, this was far lesser. He had a relatively light skin and black hair, contemporaries in this region were also partly light, partly medium tinted. A hunter-gatherer from northern Spain as recently as 5,000 BCE, tested by Olalde et al. 2014, was still dark skinned. * The arrival of Haplogroup G in EuropeIn the BalkansThe oldest G in Europe is found in Yabalkovo in Bulgaria, Lepenski-Vir in Serbia, Kargadur in Croatia, Govrlevo in Macedonia, all have range in cal BP between 5900 and 5750 BCE (11) In the Western CaucasusFrom the Maykop Novosvobodnaya culture is found in the Western Caucasus at Dlinnaya Polyana, Russia, a G2a2a2a-FGC77440+ relict, old about 3200 BCE. (12) |
|
* Starčevo and LBK Culture in HungaryFrom nearly the same period are the archaelogical finds in Starčevo in North-West Hungary and the finds of the Linear Band culture in the Carpathian Plane in Central Hungary, 6000 to 5000 BCE, old. These are the earliest settlements of the Neolithic culture in Europe. From seventeen men the Y-DNA haplogroup could be determinated. Haplogroup F is found in 23,5%, G2a in 18%, in whom, based on haplotypes, almost certainly was G-PF3147. The rest 41%, had G-L30. Total G, is nearly 60%. The others had I1-P37. (13) * Halberstadt in GermanyG2a2a-PF3147 and G2a2a1-PF3148, are found in several skeletons dated between about 7500 and 7000 years before present, in a people buried in Halberstadt, Germany. (14) 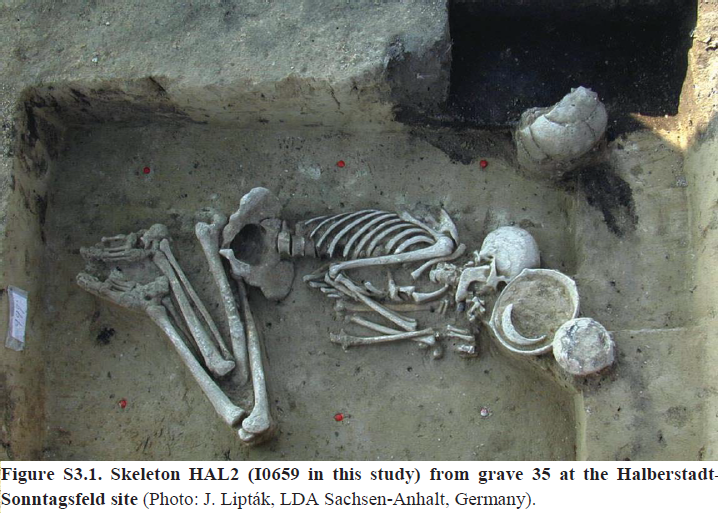
* MegalithsConstructions of stone tombs of large stones, megaliths appeared in Europe around 6,800 years ago in the Michelsberger or in the Funnelbeaker culture period. This new culture spread shortly thereafter in three waves from 6,800 to 6,200 years ago from Central Europe to northwestern France and down the Atlantic coast into the Mediterranean, Spain and to Great Britain. (15) FranceThe earliest monumental, but non-megalithic funeral architecture in Northwest France and in all of Europe emerges in the Passy graves in the Paris basin and with the necropolis Passy, which dates at the latest from circa 6960 ybp. onwards. 100 individuals from the site Gurgy les Noisats (France) are dated to the western European Neolithic around 68506500 ybp. The Y-chromosome haplogroup G2a2b2a1a2a (Z38302) is carried by 51 out of 57 male individuals and is the main male lineage of the group. Belgium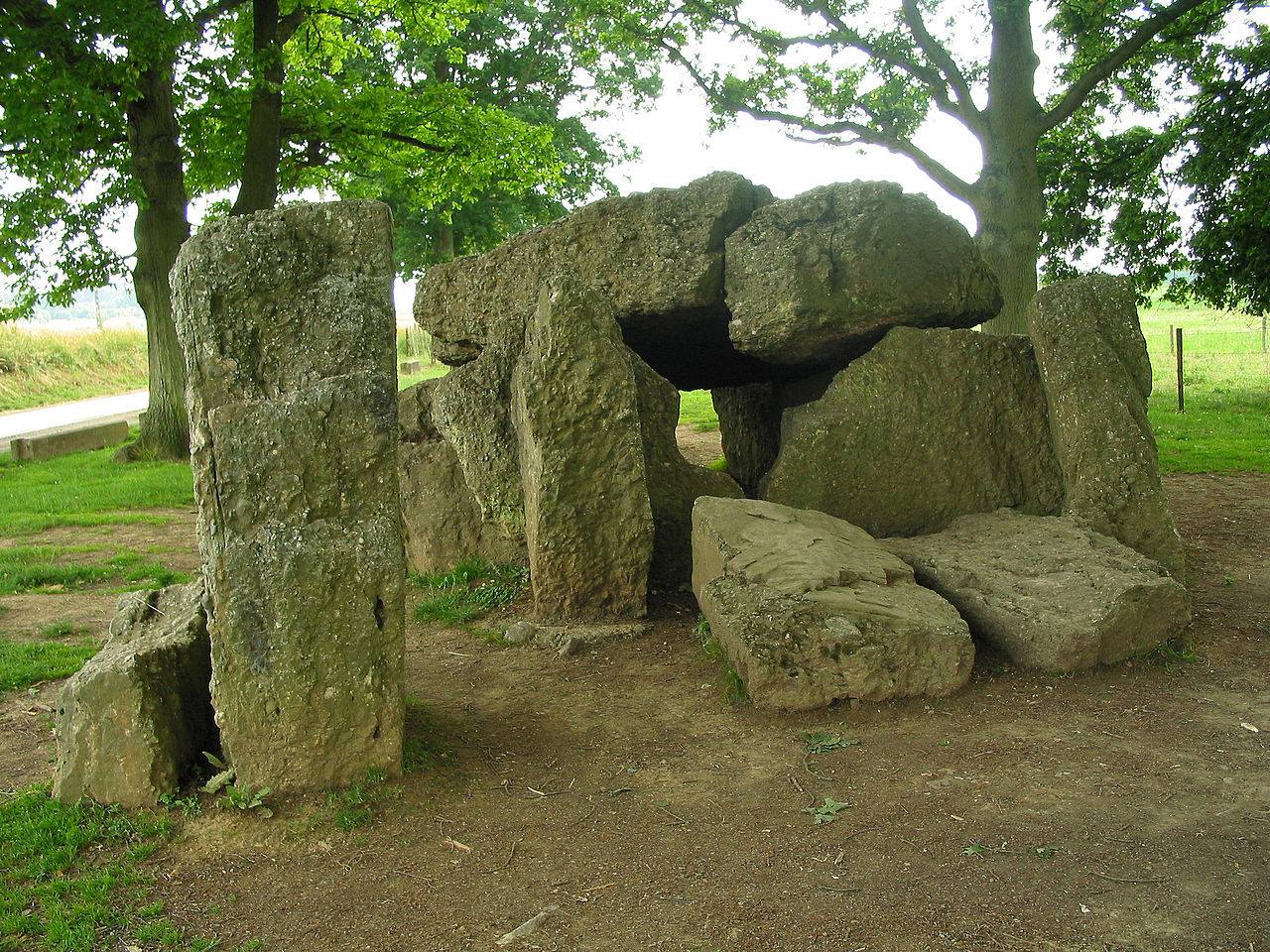
Megalithic field in Wéris, municipality of Durbuy, Belgium With 17 standing stones and two covered alleyways, spread over a length of eight kilometres. These dolmens are about 4,800 to 5,000 years old, which means that they are not as old as the Dutch hunebeds. They were built during what we call the New Stone Age by people who belonged to what archaeologists refer to as the Seine-Oise-Marne Culture. The heart of this culture was in the Paris Basin, but there were offshoots as far north as the valleys of the Maas and the Sambre and into todays Flanders and the south of the Netherlands and thought to be used as a burial site, as indicated by the discovery of the remains of fires, animal and human bones, and pottery sherds from the Funnel Beaker Culture. (15a) SwitserlandMegalithic burials from the end of the Neolithic have been found in Oberbipp and Aesch, Switserland. 
Dolmen Oberbipp, foto Denise Krieg In a dolmen burial in Oberbipp six individuals were G2a2a1a2-L91. Two of them had also G2a2a1a2a-FGC7739 and three were pre-G2a2a1a2a1a-L166*. They are dated between 3300 and 2900 BCE.
RussiaThe dolmens in the Caucasus in Russia are from at least 3250 BCE, placing them roughly in line with tail end of the Neolithic in the western Caucasus and the beginning of the Proto-Colchian culture in the Lowlands. (17) In a dolmen in the Western Caucasus is found ancient G sample, not sure it was in this dolmen, Dlinnaya I 6272, FGC77440+, a SNP in subgroup G2a2a2a-Z45970. In dolmens of the Western Caucasus bronze knives had been found which have closest analogies in the Mediterranean. (18)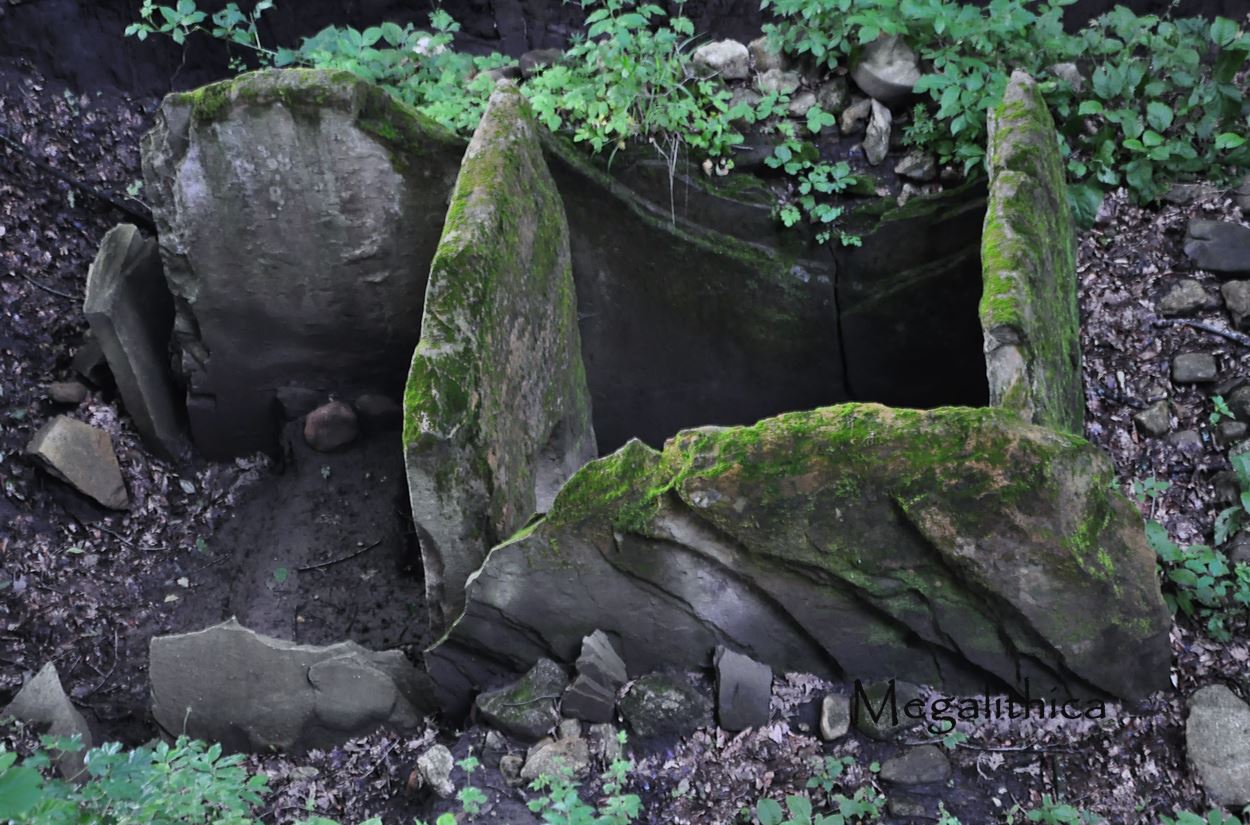 
Dolmen in the Western Caucasus NetherlandsThe oldest Dutch dolmen (in Dutch Hunebed) dates back 4,300 years ago.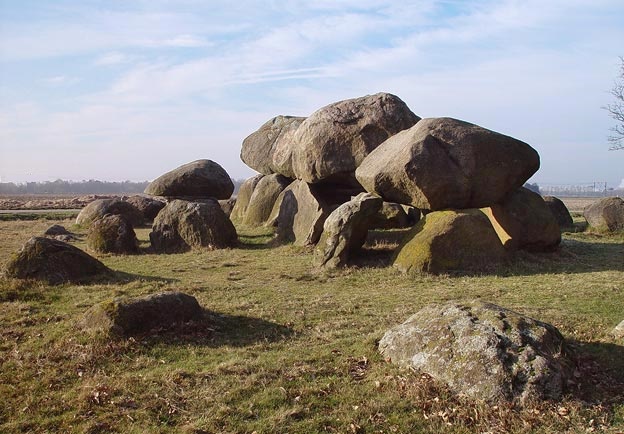 
A Dutch Hunebed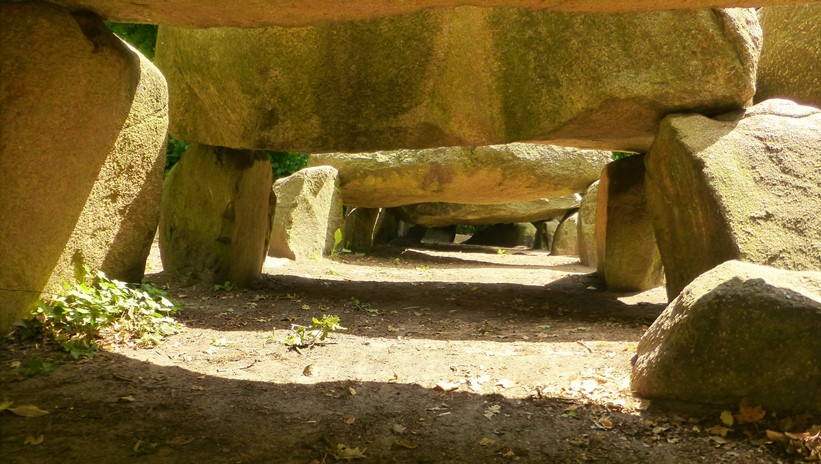 
Under a Dutch Hunebed * In England, these Burial Chambers were built for the first time a thousand years later. Sometimes they are arranged in circles; in Wales they are called Cromlech, in England Stone circle and Henge. If they occur in groups, the British call them a Cairn. Selina Brace c.s. found overwhelming support for agriculture being introduced to Britain by incoming continental farmers, with small and genetic affinities with Iberian Neolithic individuals indicating that British Neolithic people were mostly descended from Aegean farmers who followed the Mediterranean route of dispersal. (19) * Ötzthal Tirol AustriaThe thirth second oldest archaeological find of Haplogroup G, is the ice mummy who was found over a decade ago in a glacier at the edge of the Ötzthal, in Tirol in Austria. It is the mummy of a man who lived during late Neolithic times, at the beginning of the Copper Age. His age is calculated to be 5,300 years, and his genome has been well researched. His haplogroup is G2a2a1a2a1a-FGC5672. His mt-Haplogroup is K1. (20) This is the oldest human mummy, found to date in Europe and had been well preserved by glacial ice. He had brown eyes, was lactase intolerant, about 55 years old, 5 feet 2.5 inches tall, and probably a hunter. He had a very long bow with him, about 6 feet long, and fourteen arrows, some not yet finished. He also had a copper ax made of 99.7% pure copper. He wore sturdy clothes which had been patched, a hat, and shoes with soles made of bearskin. Considering this relatively expensive clothing as well as tools for hunting and working, it is thought that he may have been a leader. From the chemical analysis of his bones and teeth, one can conclude that he must have be born in the region Bolzano and during a long time of his live lived in Winschgau on the South Slopes of the Italian Alps. He had significant arteriosclerosis, a worm infection, Lyme's disease and joint disorders which may have been the result of this last infection. He had a fresh arrow wound in the shoulder and quite likely bled to death. An arrowhead was found high in his chest; the wooden arrow shaft had been removed, probably by himself. His precious belongings were not removed at the time. He had a full stomach, having recently eaten flour products and deer meat, but he had no food with him. He had rows of dashes tattooed on one knee and on his back, at the lumbar vertebrae, which possibly had a magical-medical significance. And yes, bloodstains from four other persons were found on his clothing, but nothing has yet been announced concerning these. |

Ötzi the iceman |

Reconstruction of Ötzi the iceman from the Ötzthal (21) |
|
* Dominant newcomersIt is striking that their settlements showed an increase in defensive measures. Notable are the many finds of skeletons that are buried very disorderly, so it seems that that these many people died a violent death. This indicates a violent end of this era. (22) Today haplogroup R1b1a2-M269, is dominant in Western-Europe, occurring at rates between 50% and 80%. Scholars increasingly think that this haplogroup emerged about 6.000 BCE in Asia Minor and then spread to Europe. They were the second wave of immigrants from Anatolia, bringing with them the Chalcolithic culture , the Copperage in the late Neolithic. After their arrival in Europe, a population explosion occurred within this group and within 1000 years they became the dominant group in an area stretching from Hungary to the Atlantic Ocean. During the following millennia, they pushed the resident population of hunter-gatherers to the peripheries: to the Alps, like the Iceman with his bow; to the Islands of the Mediterranean, like Sardinia; and to the UK Isles. This explains the relatively high concentrations of haplogroup G in these regions. (23) The arrival of this new population is also evidenced in the mtDNA samples, which also show a major change during this same time period: the resident mtDNA being pushed to the edges of Europe. Comprehensive population genetic analyses utilizing large databases of present-day populations have disclosed genetic affinities of the Linear Pottery Culture with the contemporary Near East, Türkiye and the Caucasus, supporting the theory of a genetic influx from this region into Central Europe at the time of the advent of farming, and explaining the apparent genetic discontinuity between foragers and farmers. (24) With the invasion of the Goths at the beginning of our era, it is assumed that the eastern Alans peoples moved to the Caucasus, to what is now Northern-Ossetia-Alania. The highest rate of occurrence of haplogroup G2a1a1-FGC693, is in the Caucasus. The question was whether this clade came in the Caucasus from the North or from the South. It is thought more and more that the latter is the case. (25) This Alan DNA is discussed along with their history on the Alans page of this website. * Old clades of Haplogroup G largely disappear from EuropeIn the Bronze Age, haplogroup G suddenly becomes rare in Europe. Shortly after 3,000 BCE new peoples came from the Pontic-Caspian steppes with new cultures, as Corded Ware and the Bell Beaker culture. They had a new Y-DNA namely R1a and R1b. This peoples caused the downfall of the agricultural population of whom the men had haplogroup G. The men were almost certainly killed. and the the women divided among themselves. This is evidenced by the disappearance of the old G Y-DNA clades from the Europa, while the mt DNA present only decreased moderately. G people survived in some remote areas as on the coasts and islands of the Mediterranean Sea, but also some new G, G-L13 and his clades, came in. (25a) * New G subgroups in EuropeG2a2b2a1a1a1a G-L13 and its clade G2a2b2a1a1a1a1-CTS9909/Z2022, were most likely part of the new peoples with the R haplogroups from the Pontic-Caspian steppes. They had probably lived there with them for a while. At least they appeared simultaneously with them in Western Europe. Their descendants still live there and they have spread further to new continents along with the other Europeans. The hunter-gatherers of Haplogroup I have largely managed to survive. |
Treilles (Fr.)25 graves from about 5000 years, ago were found in a large Neolithic burial mound in Treilles, Languedoc-Roussillon, in France. Twenty of the twenty-five men had G2a, based on their markers. This is a remarkably high rate of 80%. The other 20% had R1b, and E1b1b. All of the G men had the same haplotype, so they were closely related family members. |
| DYS Markers | 393 | 390 | 19 | 391 | 385a | 385b | 439 | 389I | 392 | 389II | 458 | 437 | 448 | GATA H4 |
456 | 438 | 635 |
| DYS value | 14 | 23 | 15 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 30 | 18 | 16 | 20 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 21 |
|
De Treille markers (26) The low percentage <2% of shared lineages between Treilles and current populations, and the fact that the ancestral and current G2a haplotypes do not seem related, imply that the G2a lineage of Treilles was probably lost between the end of the Neolithic and today. * Ergoldingen (Germany)In an early medieval grave in Ergoldingen, in Bavaria (Germany), dated round 670 AD, six men were buried together, two were G2a2, one must have been G2a2a-PF3147 because of his double DYS19 values, the other had G-Z2022, so was G2a2b2a1a1a1a-CTS9909. They were buried with their swords, spears, and shields, so they were probably knights. |
| DYS Markers | 393 | 19 | 391 | 385a | 385b | 426 | 388 | 439 | 389 I | 392 | 389 II | 458 | 459a | 459b | 447 | 437 | 448 | 449 | GATA H4 |
438 | 481 | 446 |
| 244 E | 14 | 14-15 | 11 | 13 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 29 | 16 | 9 | 9 | 23 | 16 | 10 | 21 | 21 | ||||||
| 244 F | 13 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 29 | 19 | 9 | 9 | 22 | 27 | 12 | 11 | 21 | 16 |
|
The markers of the 7th century Bavarian cavalrymen. (27) * Here is a spreadsheet with All archaeological G Ancient G-M201s with sequencing. 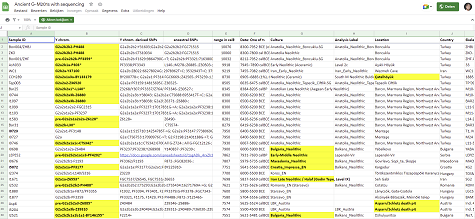
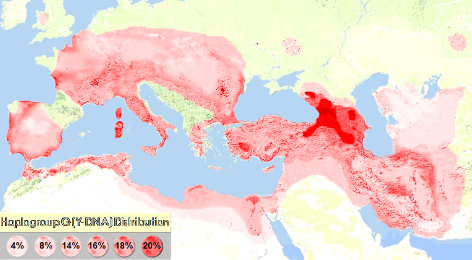
* The current haplogroup G distibution.
The haplogroup G distibution. (28) * 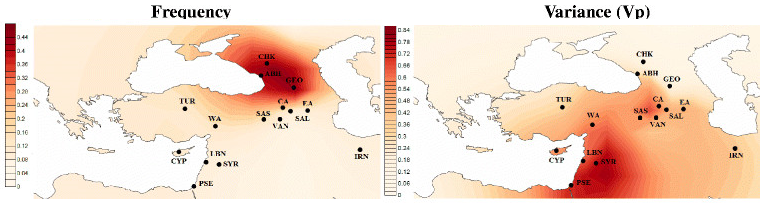
Geographical distribution map of haplogroup G Frequencies and Genetic Variances (Vp) (29) * The presence in each country of Haplogroup G in decreasing levels |
|
Northern-Ossetia-Alania |
70 % |
|
Georgia |
40 % |
|
The entire Caucasus, Kabardinia, Azerbaijan |
30 % |
|
Kazakhstan, the Kazakh Argyns, who make 20 % of the population, are the main founders of the Kazakh khanate in the 15th century. They have the highest levels of G in the world, 67%, mostly G1a. (30) |
20 % |
|
Catalonia (Sp.), and Ibiza, the Kalash people in Northern-Pakistan |
20 % |
|
Iran, Armenia, Cyprus, Crete, Croatia, the Gagauzes in Bulgaria (31) |
8-16 % |
|
Gagauzes in the Balkans and Moldova. (31) |
13,5 % |
|
Corsica, Sardinia (32) |
11 % |
|
Türkiye, Israel both Jews and Palestinians. |
10 % |
|
Italy increasing to the South: Northern-Italy 6%, Middle-Italy 9%, South-Italy 14%. (33) |
10 % |
|
Tirol (Austria) of whom 75% have G2a2b2a1b-L497, the dominant European clade. (34) |
10 % |
|
Egypt. (35) |
8 % |
|
Czech Republic, Romania. (36) |
5-6 % |
|
Spain. (37) |
5 % |
|
4,8 % |
|
|
Netherlands. (40) |
4,1 % |
|
Western-Europe, Berbers (Morocco) (41) |
3-4 % |
|
Poland: Slowakians: 4,9; Bavarians 3,2; Meckelenb. 1,5; Kociewie 0,5 (42) |
2,6 % |
|
UK, Northern-Europe, Hungary and Russia |
1-2 % |
|
* The extremely high concentration of Haplogroup G around the Caucasus is noteworthy, especially in Northern-Ossetia-Alania. It is assumed that there was an ancient European core population which belonged to Haplogroup G, but which was later repressed by Neolithic newcomers from other Haplogroups, particularly by haplogroup R1b. The G clades among the steppe peoples of southern Russia are a later replenishment. In Europe G comprises 5% of the population, in France and the Benelux this is about 4%. In Belgium, the presence of Haplogroup G, is about 10% higher then in the Netherlands, and there is a clear difference between the northern and southern parts of the Netherlands: Belgium is 4,1%, but the Netherlands is 3,7%, with most of these being found in the southern part of the country. |
|
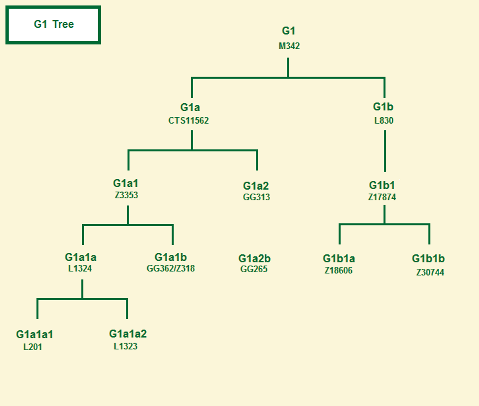
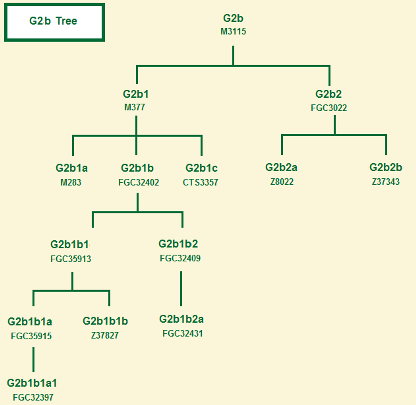
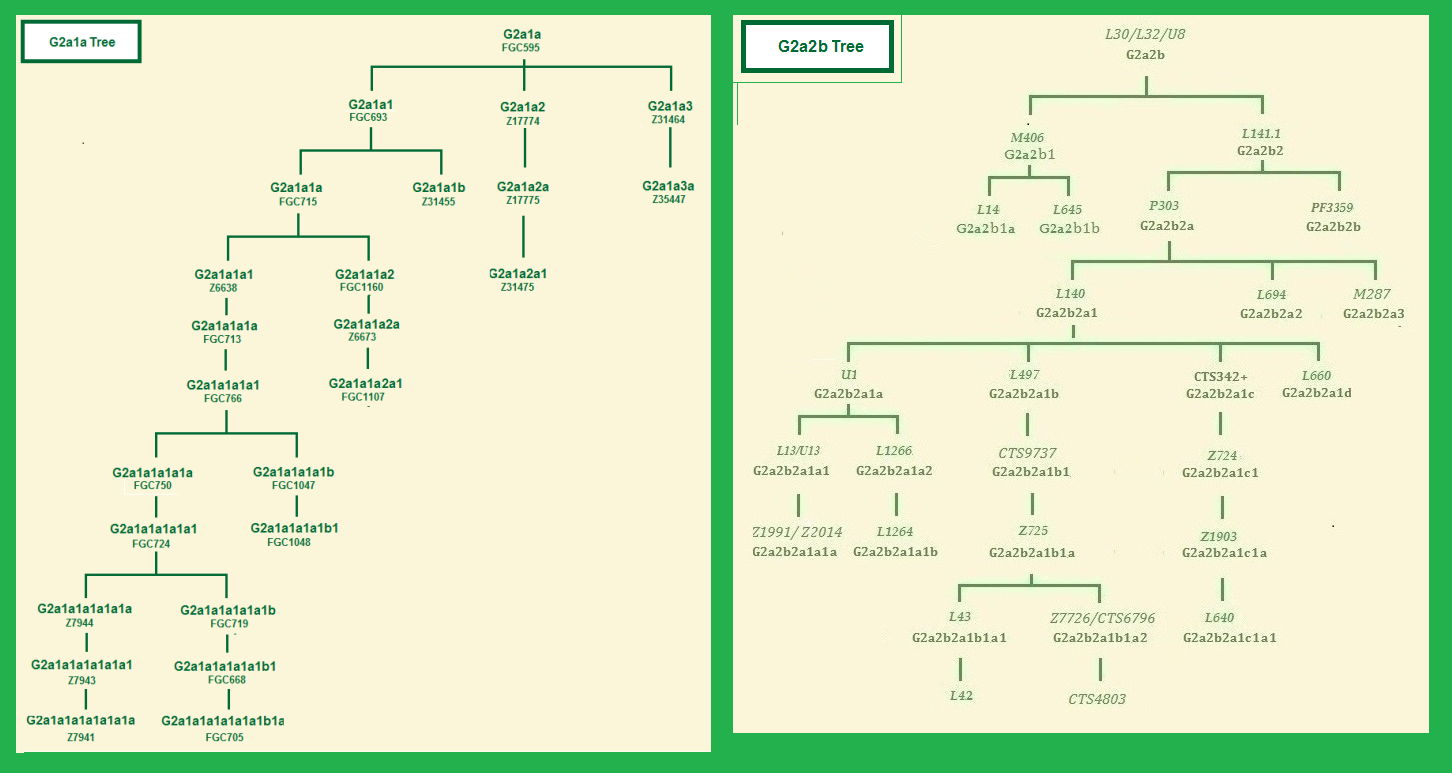
* Haplogroup G trees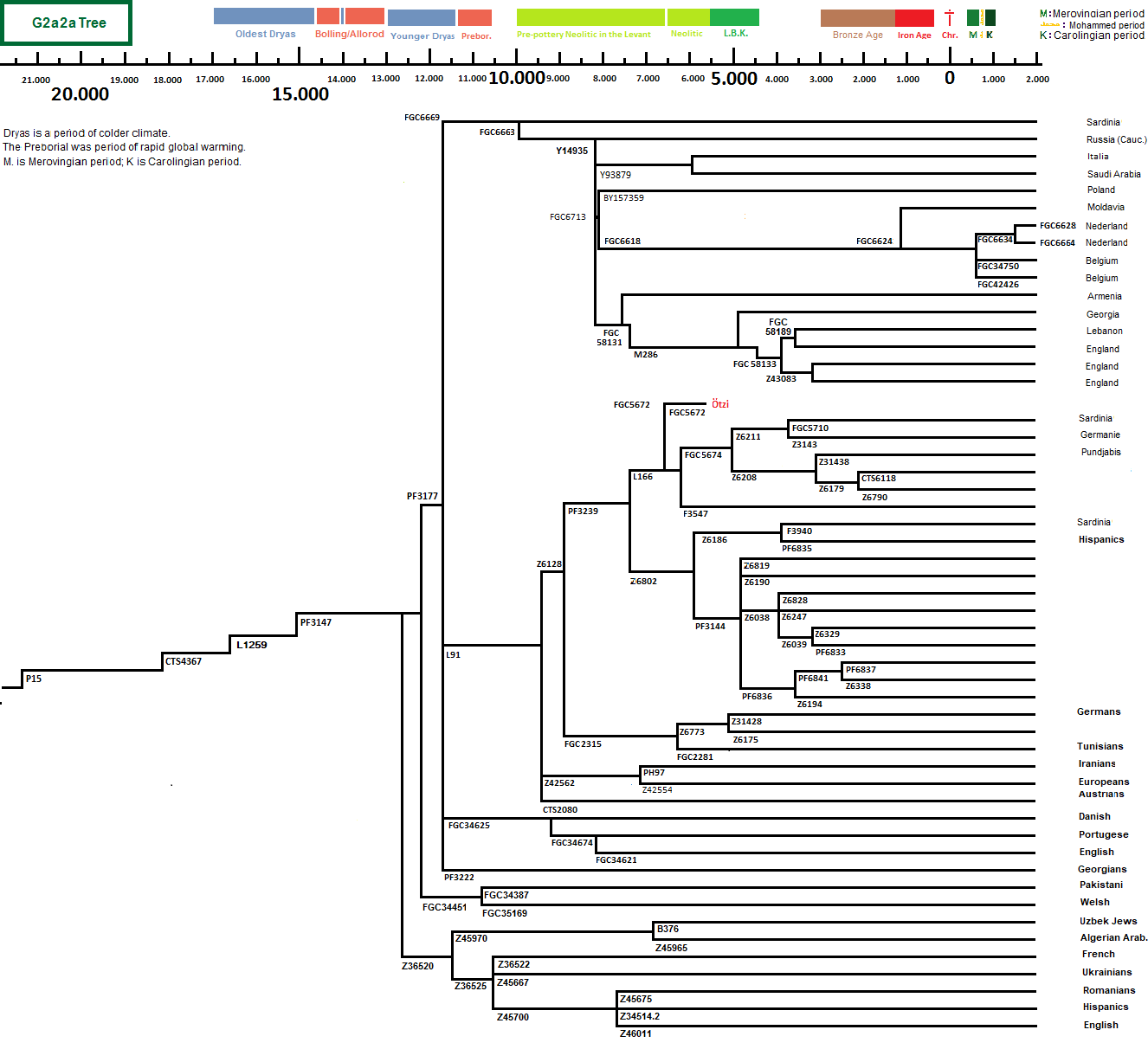
|
|
|
|
|
* Haplogroup G-M201 TreeThis is an attempt to merge the ISOGG tree and the YFull tree* G1-M342/M285, formed 26.000 ybp, TMRCA 18,600 ybp. G1a-CTS11562, formed 18.400 ybp, TMRCA 14400 ybp. G1a1-GG349/Y11751. G1a1a-BY1124/GG353, formed 14.500 ybp, TMRCA 13200 ybp, Russians, Saudis. G1a1a1-Z3353, formed 13200 ybp, TMRCA 13.200 ybp, Indians, Yemens, Slovakians. G1a1a1a-L1324, formed 13.200 ybp, TMRCA 4800 ybp and is found among Ashkenazi Jews, Bulgarians, Kazakhs, Mongols, Kuwaitis, Italians. G1a1a1a1-Y12260, G1a1a1a1a-L201, formed 2800 BCE, TMRCA 275 BCE, Russians and Ashkenazi Jews of Europa. G1a1a1a1a1~FGC39025, Kazachs and Ashkenazi Jews of Europa. G1a1a1a1a2-Z45734, Ashkenazi Jews of Europa. G1a1a1a1b-GG1, Mongols in Mongolia, formed probaly 2,000 BCE. G1a1a1a1c-Y14914, formed 3000 BCE. Kuwait, Syria. G1a1a1a1c1-PH4611, formed 1700 ybp. Kuwaitis. G1a1a1a1c1a-Z35053, formed 600 ybp. Kuwaitis. G1a1a1a1c1b-Z35057, formed 600 ybp. Kuwaitis. G1a1a1a1c2-Z35061, formed 1700 ybp. Syrians. Kuwaitis. G1a1a1a1c2-Y15524, formed 1700 ybp. G1a1a1a1d-Z44585/Z34108. G1a1a1a1e-FT107951. G1a1a1a1e1-Z45784. G1a1a1a1e2-FT107429. G1a1a1a2-L1323, formed 4800 ybp, TMRCA 750 ybp Kazakhs, Argyn. G1a1a1a2q-GG93/Y12744, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2b-GG90, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2c-GG86, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2d-FGC31603, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2e-GG76, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2f-GG81, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2g-GG65, formed 750ybp, Kazakhs. G1a1a1a2h-ZQ861, formed 750ybp, G1a1a1b-GG362/Z3189, formed 13300 ybp, TMRCA 9400 ybp, archaeological find in Seh Gabi, Iran, cal. 5100 bp, now in Iran, Slovakia, Germany, Türkiye, India (Gujaratis), n.e. Europe (Ashkenazi Jews), Bashkirs of s.w. Russia, Kazakhs, Argyn, Yemenis, Arabs. G1a1a1b1-Z26332, formed 9.400 years ybp. G1a1a1b1a-FT101799. G1a1a1b1a1-BY82294, Slovaks, formed 9.400 ybp. G1a1a1b1b-Z31487. G1a1a1b2-FT17156. G1a1a1b2a-Z31492, Gujaratis of India, formed 9.300 years ybp. G1a1a1b2b-FT19393. G1a1a1b2b1-BY62146. G1a1a1b2b2-FT19860. G1a1a2-GG313, formed 13300 ybp, TMRCA 9600 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G1a1a2a-GG167, formed 9600 ybp, TMRCA 8500 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G1a1b1a-GG162, GG169, formed 8500 ybp, TMRCA 5800 ybp, Brazil, Iran. G1a1b1a1-GG157, GG164, formed 550 ybp, TMRCA 375 ybp, Bashkirs of Bashkortostan. G1a1b1a1a-GG153, formed 375 ybp, Bashkir of Bashkortostan G1a1b1a1b-GG155, formed 375 ybp, Bashkir of Bashkortostan G1a1b1a2~BY164166/Y153532 G1a1b1b-Z44602, formed 8100 ybp. G1a1b2-GG272, formed 9200 ybp, TMRCA, 6900 ybp, Quwaitis, Saudis, Arabs. Kuwait. G1a1b2a-GG270, GG285, Y159025, formed 6900 ybp, TMRCA 6900 ybp, Saudy Arabia. G1a1b2a1-GG265, formed 6900 ybp, TMRCA 2900 ybp, Armenians Saudis. G1a1b2a1a-GG266 formed 2900 ybp, TMRCA 1200 ybp, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1-GG264 formed 1200 ybp, TMRCA 950 ybp, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1a-GG245 formed 950 ybp, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1b-GG232 formed 950 ybp, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1c-GG260 formed 950 ybp, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1c1-GG258 formed 650 YBP, Armenia G1a1b2a1a1c2-GG250 formed 650 YBP, Armenia G1a1b2a1b-Y134359 G1a1b2a1b1-GG223. G1a1b2a1b2-Z45738, G1a1b2a1c~Z45198. G1a1b2a2~BY181013. G1a1b2a3~BY175519/Y156028. G1a1b2a3a~BY190402. G1a1b2b~Z45949. G1a2-F2885, formed 14400 ybp, TMRCA 8100 ybp, lebanese, English, French, Spanish, Nepalese, Brahui, a Han Chinese. G1a2a-BY21302, Z45019, formed 8100 ybp, TMRCA 7900 ybp, UK. G1a2a1~A454,2/ZS1981.2, FGC7391.2, formed ybp, TMRCA ybp, . G1a2a2~Z45001, formed ybp, TMRCA ybp. G1a2b~BY184767, formed ybp, TMRCA ybp. G1b-L830, formed 18400 ybp, TMRCA 8400 ybp, G* (pre-G-L830*?) archaeological find in Aposelemis, Crete Greece, 6063-6014 calBCE. G1b1-Z17874, formed 8500 ybp. TMRCA 2900 ybp. G1b1a-Z18606, Belarus, Bulgaria, Ashkenazi Jews of Europa, 5.000 years. G1b1b-Z30744, formed 2900 ybp, TMRCA 550 ybp, Kuwaitis, Quataris. G1b2-BY165821, formed 18600 ybp. * G2-P287, formed 25,200 ybp, TMRCA 20,800 ybp probably in the fertile crescent.
G2a-P15, formed 20800 ybp, TMRCA 18000 ybp and started expanding after the Ice Ages, 14,500 ybp. Of the European archaelogical DNA 20% has these original clade; together with his subgroups they make 60% of the Earliest Neolithic European DNA. G2a1-FGC7535/SK1106/Z6552 (former L293), formed 18000 ybp, TMRCA 18000 ybp. G2a1-Z6552* is in an archaeological find in the Shanidar Cave in Irac. He is from 8300-7900 BCE, so about 10.100 ybp.
G2a1a-FGC595/Z6553, formed 15000 ybp, TMRCA 9500 yb (herein or in subgroups) Uyghurs, Uzbeks, Karakalpaks, Bashkirs, Kumyks, Karachays, Tatars, some among Hungarians, Czechs, and Bulgarians and Kalash and Brahui. G2a1a1-FGC693/Z6653, formed 9500 ybp, TMRCA 6700 ybp, Lebanon, 12% of the people in the North and Northwest of Georgia with a TMRCA of 7,500 BP, is of Neolithic origin in the Caucasus. spread probably with the Christian Ossetians eastward to China and Mongolia. G2a1a1a-FGC715/Z6679, formed 6700 ybp, TMRCA 6000 ybp. G2a1a1a1-Z6635, Z6692 formed 6000 ybp, TMRCA 6000 yb. G2a1a1a1a-Z6638, formed 3,900 ybp, in Ossetians, Armenians, Abkhazians, Georgians, Karachays, Lezgins of Dagestan, English, Moldavians, old 4.5 ky. G2a1a1a1a1-FGC713/Z6677, in Jasz. G2a1a1a1a1a-FGC766/Z8014. G2a1a1a1a1a1-FGC750/Z758, formed 6000 ybp, TMRCA 4300 yb, Ossetia, Türkiye, Georgia. G2a1a1a1a1a1a-FGC724/Z7940, formed 4400 ybp, TMRCA 4300 ybp, in subbranches are people from Trabzon who are likely originally of Kartvelian "Sanni" (Zan) origin and Svans. G2a1a1a1a1a1a1-Z7944. G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a-FGC3762.2. G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1-BY169049, Ossetians. G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a-Z7961, G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1-Z7944, G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a2-FGC719/GG330, Georgian. G2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2~FGC3761 G2a1a1a1a1a1a1b~Z39665 G2a1a1a1a1a1a2-FGC719, formed 4300 ybp, TMRCA 750 ybp, one Libyan and one Bulgarian. G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a-FGC668, Ossetians and Georgians. G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a1-A199/B300, formed 750 ybp, TMRCA 750 ybp G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a2-B375, Ossetians. G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a3-FGC690/GG332, formed 750 ybp, TMRCA 750 ybp, Ossetians. G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a3a~BY74776 G2a1a1a1a1a1a2a3b~FGC683 G2a1a1a1a1a1a3-Z40550, Northeastern coast of Türkiye and an Abkhazian. G2a1a1a1a1a1a3a~L267.2, Z31303 G2a1a1a1a1a1a3b~Z40552 G2a1a1a1a1a1b-Z31459, Y29585, formed 4300 ybp, TMRCA 3200 ybp, Georgian. G2a1a1a1a1a1b1-Z31461 G2a1a1a1a1a1b1a-Z45053, formed 2200 ybp, TMRCA 2100 ybp, Russia, Chechenskaya respublica. G2a1a1a1a1a1b1a1~Z31460, Z31463 G2a1a1a1a1a1b1a2~Z45048, Z45049 G2a1a1a1a1a1b1b~Y138630, Y138647 G2a1a1a1a1a1b2~Z44455, Z44456 G2a1a1a1a1a1b3~Z44788, Z44789 G2a1a1a1a1a2-FGC1047/Z7952 English G2a1a1a1a1a2a-FGC1048/Z7953, (H.) G2a1a1a1a1b-Z7955. G2a1a1a1a1b1-FGC1048/Z7953, English. G2a1a1a1a2-CTS8481.1, Moldavians. G2a1a1a1b-BY190025 G2a1a1a2-FGC1159,FGC1160, Europe (Ashkenazi Jews), Russia (Karachays, Lezgins) . G2a1a1a2a-Z6673. G2a1a1a2a1-FGC1107, Ashkenazis. G2a1a1a2b-BY186510, Karachays. G2a1a1a2b1-B296/Z31216, Karachays. G2a1a1a2b2-BY186209, Karachays. G2a1a1a2c-BY21464, Lezgins of Dagestan. G2a1a1a2c1-Z29313, Lezgins of Dagestan. G2a1a1a2c1a-Z29311, Lezgins of Dagestan. G2a1a1a2c1b-Y47534, Lezgins of Dagestan. G2a1a1a2c2-Z45585, Lezgins of Dagestan. G2a1a1b-Z31455, 4.5 KY. G2a1a1b1-BY65507, Z31456, 4.5 KY. G2a1a1b2-Z25119.2, Y7015, 4.5 KY. G2a1a1b2a~Z43193 G2a1a1c-FGC65315 G2a1a1c1~Y36036 G2a1a1c2~BY201477 G2a1a2-Z17774, formed 9500 ybp, TMRCA 6100 ybp, Italy, England, Pakistan (Punjabis). G2a1a2a-Z17775, Punjabis of Pakistan, Spaniards, Italians. the Dutch family Pennings having a 13th century ancestor van der Straetten in Oirschot, Brabant and Italians, 7.0 KY. G2a1a2a1-Z31475, Punjabis of Pakistan. G2a1a2a1a-Z31469 G2a1a2a1b-Z39928 Italians. G2a1a2b-Z31451, English, 7.0 KY. G2a1a3-Z31464, Z35444, formed 9500 ybp, TMRCA 3200 ybp, Netherlands, Germans. G2a1a3a-Z35447,Germans, 3.0 KY. G2a1a3a1-Z35443,Germans, 3.0 KY. G2a1a3b-FGC50490, G2a1a3b1~Z34465, G2a1a3b2~Z46159, G2a1b-Z30702, Germans, age 16,200 years. * G2a2-L1259, age circa 18,200 yrs, from which two lines with a TMRCA of 17.000 ybp: G2a2a-PF3147, and G2a2b-L30. * G2a2a-PF3147, formed 17.800 ybp, TMRCA 12.800 ybp, is the smallest of the two subgoups of G2a2. It has with its subgroups 10% of the European G. It arose probably in what later became the first Neolithic areas of Anatolia and spread with other G groups, G-L30 and subgroups, ca 8000 ybp mostly around the Mediterranean along the South and the North coasts and the Islands as Sardinia and Corsica, and in the Balcans and Bulgaria. This is nowadays found in low percentages eastwards to Iran and Azerbaijan. However it is absent in the North Caucasus.
G2a2a_PF3147 and its clades, are also treated on the Clade G2a2a page of this website. G2a2a1-PF3148, formed circa 12,800 ybp, TMRCA 12,100 ybp, many archaeological finds, in Halberstadt in Germany circa 7000 ybp, Calvados in France 6.400 ybp, Oberbipp in Switzerland 5.300 ybp, Dlinnaya Polyana in Russia, 5.200 ybp, Alto de la Huesera in Alava, Basque country in Spain, 4.950 ybp. Today in Wales (Roberts) and Pakistan. G2a2a1a-PF3177, formed 12,000 ybp, TMRCA 11.500, ybp. PF3177* is in Italies Retic Alps, Sardinia, an English American and an Egyptian. Archaeological finds in Ukraine, Serbia, Croatia, France. * G2a2a1a1-FGC6669, formed 11.800 ybp, TMRCA 9.900 ybp. It looks that this clade did not take part in the entry into Central and Western Europe in the beginning of the Neolithic, but remained in the eastern region of the Mediterranean. In Roman Time they assumely spread over the Roman Empire. FGC6669* are an Italian from Sardinia and a Russian Adygean. G2a2a1a1~FGC6619, FGC6663, formed 10.000 ybp, TMRCA 8,200 ybp, one known FGC6663* is from the Krasnodar district (Краснодарский край) in the Northern Caucasus in Russia. G2a2a1a1~Y14935, formed 8.200 ybp. TMRCA 8,200 ybp, One known Y14935* is an Saudi Arabian. G2a2a1a1a-FGC58131, formed 8,200 years before present, archaeological finds 2.700 ybp in Swat Valley Pakistan, nowadys one Armenian family. * G2a2a1a1a1-M286, formed 7,000 ybp, TMRCA 4,400 ybp, now in Türkiye, Georgia, Cyprus, Lebanon, Syria, Armenia, Germany (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern), France (Strasbourg) England and Scotland. G2a2a1a1a1~FGC58127 formed 4,400 ybp. TMRCA 3,300 ybp G2a2a1a1a1a-FGC58189, G2a2a1a1a1a1~FGC58118 Suffolk, England. G2a2a1a1a1a2~FGC59473 formed 3,000 ybp, TMRCA 1200 ybp., Syria and Lebanon. G2a2a1a1a1a2a~FGC59474 Lebanon (E.C.) G2a2a1a1a1a2b~BY193531 Oman (Q). G2a2a1a1a1b-Z43081 England. G2a2a1a1a1b1-Z43083 England, formed 3300 ybp, TMRCA 600 yb. G2a2a1a1a1b1a-Z43083 BY123198, Y70685, formed 600 ybp, England. G2a2a1a1a1b1b-Z43083 FGC60946, England, formed 600 ybp. G2a2a1a1a2~BY61119. * G2a2a1a1b-FGC6713/Y14984, formed 8100 ybp, TMRCA 8100 ybp, Armenian (Mugumov). G2a2a1a1b1-FGC6624, formed 8100 BCE and TMRCA 1100 BCE, Moldavian (Ghemu). G2a2a1a1b1a-FGCC6618/FGC6634, formed 500 CE, TMRCA 500 CE, Benelux line. G2a2a1a1b1a1-FGC6628, formed 1500 CE, Dutch (Marres). G2a2a1a1b1a2-Y89939, formed 1500 CE, Dutch (Mares). G2a2a1a1b1b~FGC34750, formed 500 CE, Belgium (Nolet). G2a2a1a1b1c~FGC42426, formed 500 CE, Belgium (Slootmaekers). G2a2a1a1b2~BY157359, formed 5,500 ybp, TMRCA 50 CE, Poland and an Sephardian. G2a2a1a1b3-Y93879, formed 7,500 TMRCA 5,400 ybp, Italian and Saoudi Arabian. * G2a2a1a2-L91, formed 11,800 ybp, TMRCA 11,800 ybp. In Greece archaelogical finds are in Kleitos dated 6,100 ybp and in Bulgaria 4,759 ybp, in a dolmen burial in Oberbipp (Schweiz)) six individuals were G2a2a1a2-L91. They are dated between 3300 and 2900 BCE.
This clade is now also found among the Bakhthiari nomads of Iran and, in Northern India, an Uyghur from China, in Czechia it is 3%. Some in the Netherlands, Germany Alsace-Lorraine, Britain and Scandinavia and Maharashtra Brahmins. G2a2a1a2a-Z6484, Z6488, FGC7739, archaeological find in three individuals in Barcin Höyük, Türkiye, 8,300 ybp, one find Bulgaria from 7.900 ybp, one in a find in Croatia from 4.700 ybp. In a dolmen burial in Oberbipp Two individuals had G2a2a1a2a-FGC7739, dated between 3300 and 2900 BCE.
G2a2a1a2a1-PF3239, Z6128, Z6490, formed 10,900 ybp, TMRCA 10,000 ybp in an archaeological find in a Bell Beaker individual in Hungary from 3,700 ybp, Nowadays in Switzerland, Sardinians, Armenians, and a Dutchman in Limburg. G2a2a1a2a1a-L166, S10301, formed 7000 ybp, TMRCA 6800 ybp, came in Europe probably with the Bell Beaker culture. In a dolmen in Aesch ten individuals were found with pre G-L166*. They are dated between 5100 and 4800 ybp. (45) Is now found in Bulgaria, Germany in Frankenland and Bavaria (Krause family), in Swiszerland, in Greece on Lemnos, in Italy on Sicily and Sardinia and in France on Corsica and Pakistan. (46), and in the Pundjab of Pakistan. |
|
G2a2a1a2a1a1-FGC5672, formed 6500 ybp, TMRCA 6100 ybp, found in the mummy of the Ötzthal in Tirol, Austria, a man who lived there 5,200 ybp, in the Chalcolithic, the copper Age, popular named Ötzi.
Reconstruction of a man found in a glacier in the Alps (47) |

|
|
* G2a2a1b-FGC34434, formed 12.000 ybp, TMRCA 12.000 ybp. Is found in archaeologic finds among the Early Neolithic Farmers of Halberstadt-Sonntagsfeld in Germany, 7.211-6.963 ybp and (klei10) in Kleitos, Greece 6.100 ybp .
G2a2a1b1-FGC34436, formed 12.000 ybp, TMRCA 11.000 ybp, in archaeologic finds Czechia 6.350 ybp. G2a2a1b1a-Y85489, formed 11.000 ybp, TMRCA 2300 ybp, Welsh (R.) G2a2a1b1b-G-SK1120, formed 11.000 ybp, TMRCA 3400 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G2a2a1b1b1-G-FGC34430, Pakistan (Azad Kazmir). G2a2a1b2-FGC34387, formed around 10.900 ybp, in Dravidian-speaking Brahui cattle herders and the Punjabi-speaking Pakistani (Khan). * G2a2a2-Z36520, formed 12.800 ybp, TMRCA 12.000 ybp. At Tepecik Ciftlik in Türkiye is an archaeological found dated to 6635-6475 BCE, and one from Sappali Tepe in Uzbekistan dated to 2000-1600 BCE. G2a2a2a-Z45976, BY37100, Z45970, formed 10.600 ybp, TMRCA 10.600 ybp. TMRCA 6.800 ybp, There is an archaeological find in a dolmen in the Western Caucasus, Dlinnaya I 6272, FGC77440+, a SNP in subgroup G2a2a2a-Z45970, dated to 5250 ybp.
G2a2a2a1-B376, Uzbek Jew. G2a2a2a2-Z45965, Algeria Arab. G2a2a2b-Z36525, formed 13100 ybp, TMRCA 10000 ybp. G2a2a2b1-BY37102, Y106682, formed 10000 ybp, TMRCA 8300 ybp, North Africa Berber, Bahrain, China. G2a2a2b1a-Y90753 formed 5900 ybp, TMRCA 5900 ybp. G2a2a2b1a1-Y83453, Z36522, France. G2a2a2b1a2-Z46081, Bahrain. G2a2a2b1a3-BY193093(H.). G2a2a2b1a3a-BY193216. G2a2a2b2-Z45667, TMRCA 4200 ybp, Ukrainians. G2a2a2b3-Z45700, formed 10.000 ybp, TMRCA 3.000 ybp G2a2a2b3a-Z45690, formed 3000 ybp, TMRCA 2600 ybp. G2a2a2b3a1~Z45683 G2a2a2b3a1a~BY37106, formed 2600 ybp, TMRCA 2200 ybp G2a2a2b3a1a1~Z45715, formed 2200 ybp, TMRCA 500 ybp G2a2a2b3a1a1a~Z45714, G2a2a2b3a1a1a1~Z34514.2, TMRCA 400 ybp, Puerto-Ricans from Spain. G2a2a2b3a1a1a2~BY129845, G2a2a2b3a1a1b~BY207765, BY207748. G2a2a2b3a1a1c-FT19778, G2a2a2b3a1a1c1~FT18864, FT19555, Y164204. G2a2a2b3a1b~BY70232, Romanian (Tug.). G2a2a2b3a2~BY192915, Greece (Pap.). G2a2a2b3b~Z46011, English (Tur.). * G2a2b-L30/PF3267/S126, formed 16700 ybp, TMRCA 14400 ybp, is the largest of the two subgroups of G2a in what later became the first Neolithic areas of Anatolia. In the Neolithic this clade is found in 60% of the Europeans, nowadays in only 5% of them. G-L30* is in Greece and Croatia and in some Uralic-speaking Mordvins from Russia. G-L30 is divided into two clusters:
The predominantly Southern European, Mediterranean and Levant groups. G2a2b1-M406/PF3285, formed 14400 ybp, TMRCA 8700 ybp, originated in Türkiye 14.900 ybp, and entered Italy probably about 5,000 ybp. This is the clade of Asia Minor and Southern Europe. Of the G men in Iraq, Türkiye, Greece and the Balearic Islands, about 50% belong to this clade; in Georgia, 25% (G2a1a is almost 8%); in Italy, 20%; in Spain and the Netherlands, 15%; in Switzerland, 8%; Iran, 6%; and in Poland and UK, 4%.
G2a2b1-M3310/PF3299, Mediterranean, Greeks, Italians, Lebanese, Georgians, Armenians, Azerbaijans, Turks. Austrians G2a2b1a-FGC5089, G2a2b1a1-FGC5081. G2a2b1a1a-L14/U16, formed 7900 ybp, TMRCA 5300 ybp, in Middle Easterners, Italians, Sardinians, English, French, Netherlands, Qatari. G2a2b1a1a1-Z17083. G2a2b1a1b-Z17887/Y6222, formed 7800 ybp, TMRCA 6600 ybp, Türkiye. G2a2b1a1b1-Z17886, formed 6600 ybp, TMRCA 6400 ybp, Türkiye. G2a2b1a1b1a-Z37368, formed 6400 ybp, TMRCA 5500 ybp. Germany, Italian. G2a2b1a1b2-L645, PH942, formed 6600 ybp, TMRCA 5500 ybp, Türkiye. G2a2b1a1b2a-Y134757, formed 5500 ybp, TMRCA 5000 ybp, Türkiye (Armenians, Swiss, and Germans (?). G2a2b1a2-M3302, Türkiye (Armenians), Pakistan (Pashtuns), Italy, U.K. G2a2b1a2a-M3422. G2a2b1a2a1-M3240, Shangdong Province, China. G2a2b1a2a2-BY8759, BY81131. G2a2b1a2b-Z31412. G2a2b1a2b1-BY21758/Z44794,. G2a2b1a2b1a-BY21760 G2a2b1a2b1a1-M5843 G2a2b1a2b1a2-BY69342 G2a2b1a2b1b~Z44800, G2a2b1a2b2-Z46344 G2a2b1a2c-FT56736 G2a2b1b-PF3293, age 8,700 ybp, Middle East, Sardinia, Kazakhstan (originally from Ukraine), Palestinians and Sephardic and Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b1b1-PF3296/PF3316, age 7,300 years, in Iran, Kazakhstan (Russia), Druzes, Italians. Sardinians, in the Netherlands, Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b1b1a Z30795. G2a2b1b1a1-Z30793. G2a2b1b1a1a~PF3286, Sultans Ba'Alawis of Yemen, Sultans of Siak on Sumatra-Indonesia, Richard III of England, so probablement les Maisons de Plantagenet et d'Anjou. G2a2b1b1a1b~Z31533. G2a2b1b1a1c~CTS430 G2a2b1b1a1d~Z40727. G2a2b1b1a2-S11415, Sardinians. G2a2b1b1a2a~FGC41470 G2a2b1b1a2a1-Z6029, Malta (?) G2a2b1b1a2a1a-Z31414, Sardinians. G2a2b1b1b2a1b-Z6349. G2a2b1b1b2a1c-FGC41428. G2a2b1b1a2a2-S9591, formed 5300 ybp, TMRCA 3800 ybp. G2a2b1b1a3-Z40727. G2a2b1b1b-Y2612. G2a2b1c-Z6340. Sardinia. G2a2b1d-CTS8450/S4387, Palestinian territory. The predominantly central and western European groupsG2a2b2-CTS2488, formed 14400 ybp, TMRCA 14400 ybp, most of the Europeans of west and central Europe belong to this clade. It is also found among the Brahmins in India. G2a2b2a-P303, formed 14400 ybp, TMRCA 11600 ybp, the majority of the G men in Europe, belong to his subgroups. Low rates are found in Iran, Pakistan and in the Middle East. It has also been seen among the Brahmins, in India and with an certain haplotype in Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b2a1-L140/S316, formed 11600 ybp, TMRCA 10900 ybp, the whole group with clades is the dominant G group in Europe, present in almost 80%, of G men. The first ones came into Europa probably around 8,500 ybp, archaeological find, 8000-7500 ybp of Koros neolithic in Törökszentmiklos Tiszapüspöki Karanycs, Hungary. Their number is now approaching 7% of the population in some European countries, however the average is about 3%. It is present in small amounts in some parts in France at 5% and in Italy it reaches 9%. There is an Ashkenazi cluster in northwestern Europe. G-L140* are in The Netherlands, Norway, Spain, the Carpathian Mountains, in Palestinians, Saudi Arabia and in the Dravidan speaking Brahii. (49) G2a2b2a1a-PF3346 formed 10900 ybp, TMRCA 10900 yb archaeolgical finds in Bodrog-keresztur Romania 6150 ybp and of Baden culture in Budapest Hungary 5300-4850 ybp and more. Nowadays in Rajput in India. G2a2b2a1a1-PF3345 formed 10900 ybp, TMRCA 10600 ybp Archaeological finds dated 7,000 ybp in Essenbach-Ammerbreite, Germany, LBK culture, early neolithic and in Croatia in Poland and Switserland. G2a2b2a1a1a-FGC7568 G2a2b2a1a1a1-U1/Z6779, formed 10600 ybp, TMRCA 10500 ybp. The early years of U1 seem to have been during the hunter-gatherer period, before historical records were kept, so little can be said about it until scientists are able to identify U1 subgroups in ancient skeletons from that time period. The more recent aspects of the historical period are covered in the discussions of the subgroups.
G2a2b2a1a1a1a-L13/U13/L78, formed 10500 ybp, TMRCA 4800 y. In an archaeological find in Barcin Höyük N-W Türkiye dated about 8300 ybp. In its subclades, TMRCA 4800 ybp, it is found among Germans, French, Swiss, northern Italians, UK an Ukraine, Belarus, Western Caucasus, Georgia, Armenia, and in small amounts outside Europe in Iranian Azeri, Arabs, Druze of the Levant, Palestinians in Lebanon and Syria and Sephardic Jews.
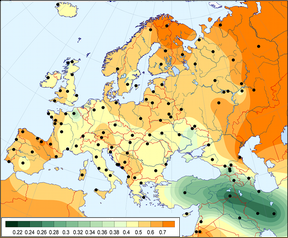
G2a2b2a1a1a1a1-Z2022, PF6860, formed 4800 ybp, TMRCA 4000 ybp, they most likely came in Western Europe in the Bronze Age, together with the R1a and RIb population. Most known samples come from Europe. The percentage in G samples in Europe is: Germany 16%; Italy 11%; the Netherlands 10%; France 10%; Poland 9%; Spain 9%; Ireland 6%; England 5%; Switzerland 4%. Some Arabs from Bahrain, Persian Jews from Afghanistan and Morocco berbers. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a-FGC995, formed 4100 ybp, TMRCA 4000 yb, has a heavy concentration in Europe. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1-FGC998/Z6764, has a heavy concentration in Europe also in the Netherlands, in Cyprus, Bahrain, Arabs, Algerians, Berbers in Morocco; (Meh). G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a-FGC1016. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1-S9751/Z6159. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a-Z29424, formed 3,600 ybp, TMRCA 3200 ybp, Germany, Swiss (Beyeler), Italy, Italian Alps (Herbet), Cypress. Poland, Jews, Hispanics, Syrians, Kurdish, and Persians. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1-L1263, Z38848, formed 3800 ybp. TMRCA 2500 ybp, Türkiye, UK. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a-Z38846, formed 2500 ybp, TMRCA 1350, Germans, Austrians, Dutch. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1-BY48807, Y19317/Z38847. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a-Y19318/Z38856. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1-Z38853 formed and TMRCA 1350 ybp, Germans. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a~FGC18956.2, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1b~Z38862, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1c~BY132524, Y15226, Z39253, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a2~Z42389, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a3-Z43288. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a3a~FT138572 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a4-43941. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a4a~Z43938 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a5~Z45662, Z45663, Z45664, Z45665, Z45666 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a6~BY202470, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a7~BY158135, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a8-FT34806. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a9~BY93933, FT79420 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a10-BY37125. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1a1b~BY164537 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1b~L1261 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a1c~S8385, Z43898 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2-Z30777. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2a-Z30781, formed 3.300 ybp, TMRCA 2000, UK. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2a1-Z38455, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2a1a~Z30778 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a2a2~Z31561 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a3~Z31368 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a4~Y46407, Z31373, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a5-Z39053 formed 3500 ybp, TMRCA 3500 ybp, Bulgarian, Georgia, Deutschland, U.K., Circassian, Kabardino-Balkarskaya (A.Q.). G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a5a~Z34070 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a5b~BY148992, FT70703. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a6~FGC31395, FGC31398 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a7~Z6406, Z6407, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a8-Z43944, BY37082, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a8a~Z43943, Z43945 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a8b-BY46240/Z46155, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a8b1~Z46154 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a9-Z44047, BY93576 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a9a~BY74257 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a9b~BY205841, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a10~M11790, Z44590, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a11-Z45562, Y134554, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a11a~Y134561, Y134566, Z22424.2 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a11b-FT24243 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a12~Z45648, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a13~Z46221, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a14~Z46290, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a15~BY174878 G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a16-BY45246, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a16a~ BY121129, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a1a17-FT167239, G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a2 Z39373. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1a2a Y45819. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a3a2a1 Y57313. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a1b Z42471. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1a5 Z38875. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1b Z44912, England. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1b1 Z30831. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1b2 Z44913. formed 4100 ybp, TMRCA 275 ybp, Ossetians, Chechchen Rep. (Russia). G2a2b2a1a1a1a1c S20738, Y51821, Z38837, Z38840. G2a2b2a1a1a1a1d~Z31362 G2a2b2a1a1a1a2~Z32842.2, Italy. * G2a2b2a1a1a1b-L1266, formed 10500 ybp, TMRCA 6700 ybp, includes half of the West Caucasians, like the Adyghes, Abkhazians, Circassians, Kipchaks, Abazins and Karbardinians and Georgians. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1-L1264, formed 4.800 ybp, TMRCA 4.300 ybp, they most likely came in Western Europe in the Bronze Age, together with the R1a population, now in Russia (Kabardinians), in the northwestern Caucasus, primarily among the Adyghians, Ossetians, Tetchens and Senkelens of Central Russia and the Urals, and in Hungary. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a-Z44222, Adyghes G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a1-L654.2, Germans. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2-Y32599/Z44227, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2a-Y32599, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2a1-y32597, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2a2-ft8486, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2a3-FT104071, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2b-FT49803, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a2b1-FT49834, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3-V7991.2, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a-Y112447, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1-FT13327, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1a-FT12699, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1a1-FT12508, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1a2-FT6767, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1b-FT69159, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1a3a1b1-FT69517, G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b-FGC21495, formed 4.300 ybp, TMRCA 3.900 ybp, Belgians. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1-S9409, formed 4200 ybp G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1~FGC21523. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1a~FGC21494 Belgians, formed 4.000 ybp. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b-Y142068. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b~-FT69475^^. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b1-BY168175. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b1a1-BY166419. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b1a1a~BY165872. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b1a2-FT238907. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b1a2a~Z31275 Kabardinians, formed 4.000 ybp. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b2-FT69558, FGC54492. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b2a-BY54724, Y76392. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b2a~FT69500. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b1b2a1~FGC14454'. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b2-Y30992/Z44144. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b2a-Z30715 Russians, formed 3400 ybp, TMRCA 3000 ybp G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b2a1~Z30713. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b2a2~Z44149. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1b2b~MF15669. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c-BY109806,. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c1-BY79584, Z45660. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c1a~Z45658. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c1b~FT80084. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c2-BY4191. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c2a~BY201471. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c3-FT145691. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c3a~FT145939. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c3b~FT152088^^. G2a2b2a1a1a1b1c4-Y142013 G2a2b2a1a1a1b2-PH1780, formed 6700 ybp, TMRCA 4500 yb, Georgians, Armenians. G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a-PH311.1, y18376, formed 2400 ybp, TMRCA 2200 yb, Chechenskaya, Georgia, UK, Türkie, Uzbekistan G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a1~Z37864. G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a2~Y48477. G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a3~BY81412. G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a4-Y128514. G2a2b2a1a1a1b2a5-Y129649 formed 2200 ybp, TMRCA 375 ybp, Chechenskaya. G2a2b2a1a1a1b3-Z6922, Z6153, formed 6700 ybp, TMRCA 3800 ybp, Sardinia, Ukraine, Kazachstan, China. G2a2b2a1a1a1b4~Z6391. G2a2b2a1a1a1c~Z39803. G2a2b2a1a1a1d~SK1154. Palestinians, prov. Hamerkaz in Israel. G2a2b2a1a1a1d1~PH4105. formed 1150 ybp, TMRCA 1050 ybp, Palestinians, prov. Hamerkaz in Israel. G2a2b2a1a1a1d2~Z45652. * G2a2b2a1a1b-L497/S317/CTS1899/PF6851/Z738, formed 10600 ybp, TMRCA 7200 ybp, This is the largest European subgroup, to which half of the European G, belongs. It seems that G-L497, which is one of the most "European" of haplogroups, spread out from Western Anatolia (where it's found in small numbers) to the Danube Basin with the First Farmers, around 8400-7800 ybp. So far, the earliest branches of L497 are found in Italy and the Netherlands. The Anatolian and Aegean L497s are more "derived" (further down the tree in G-Z725), This group is distributed as follows: Tirol 80% of the G samples; Switzerland 75%; Spain, France and Germany 60%; UK 52%, the Netherlands and Italy 44%. They formed the first wave of farmers entering Europe who started the Neolithic, recognizable by the LBK culture.
G-L497 frequenties in Europe. (50)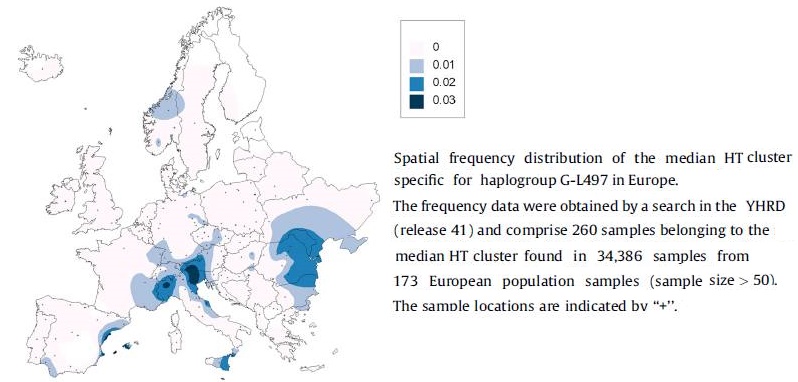
G2a2b2a1a1b1-Z1815/CTS9737, formed 7300 ybp, TMRCA 6400 ybp, archaeolgical find of Baden culture in Budapest Hungary 3300-2850 BCE and Stockholm (Sweden) ca 955 CE. G2a2b2a1a1b1a-CTS11352/Z1817,, formed 6200 ybp, TMRCA 4600 ybp, is found throughout Western and Central Europe, and especially in Germanic countries. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1-Y7538/Z725, is formed 6400 ybp, TMRCA 4600 ybp. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a-AMM042/CTS2230/Z1823, formed 4600 ybp, TMRCA 4600 ybp., archaeolgical find in Varnham Sweden 975 CE. Nowadays in Norway and Denmark. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1-L43/S147, formed 4600 ybp, TMRCA 3800 ybp, archaeolgical find in Kopparsvik, Gotland Sweden 1050 CE.. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a-L42, formed 3800 ybp, TMRCA 3800 ybp. Spain, is found in a Trypillian outlier individual. This branch might have been assimilated by Proto-Indo-Europeans through contact with the Late Trypillian people who moved to the Pontic Steppe and merged with Yamna tribes. It would later have spread around Germanic and Celtic countries alongside haplogroup R1b. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1-Y11074/Z30641, Y10621/Z30642, formed 3800 ybp, TMRCA 3600 ybp. Italia, Switserland, Deutschland, Croatia, Finland. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a-Y11076, formed 3800 ybp, TMRCA 3500 ybp., Hungary, Austria,Switserland. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a1-Z27266/F1300.2/M1809.2, Norway. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a1a-Z39505. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a1a1-Z39504, Z41264 formed 1650 ybp, TMRCA 550 ybp, Norway G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a2-CTS7357. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1a3-z31316. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1b-YSC0000033, Z41202. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1b1-Z39501. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1b1b-Y128028, Serbians. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a1c-45255, archaeologic find 300 CE, München Bavaria. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a1a2-Z40854. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a2-CTS6796/Z726, CTS35/Z6382. G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a2a-CTS4803, Z3441, formed 4.600 ybp, TMRCA 3,4000 ybp, Archaelogical finds in Hallstatt culture DA112 Czech Republic ca 2.430 ybp G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a2a1-S2808, formed 3,400 ybp G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a2a1b-FGC8304/Y3098, Archaelogical finds. One in Magdalenenberg (Dld.) in a rich elite grave, clearly a nobleman. He was a considerably tall individual. He had a left tibia with healed periostitis and his vertebral column had degenerative alterations. The second in Ludwigsburg Römerhugel (Dld.) both ca 2.500 ybp and Hallstatt Culture. (51) G2a2b2a1a1b1a1a2a2-Z30771, Z16029.2 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b-FGC477/Y8903 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b1-FGC489/Z6748, G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b1a-FGC490 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b1a2~Z40857 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b1a3~BY105807 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2-BY27899.1, BY27900, G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2a~Z31348 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2b-BY124520 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2b~BY37046 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2b1~Z45475, G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b2b2-BY113713 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b3~BY180233 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1b4~A2864.2 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1c-FGC807 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1d~CTS718 G2a2b2a1a1b1a1e-Z39863 G2a2b2a1a1b1a2-Z6911 G2a2b2a1a1b1b-S10458, Italy, France, Poland (nobility), Germany, Netherlands (Gelre, Limb). G2a2b2a1a1b1b1-Z24311, G2a2b2a1a1b1b1a-Z24316. G2a2b2a1a1b1b1a1-Z31358, UK. G2a2b2a1a1b1b1a2-Z31352, Germany. * G2a2b2a1a1c-CTS342, originated about 10,5 KY ago somewhere in Anatolia or the Fertile Crescent. Spread soon in all directions. Is found in archaeological remains dated 8,600 ybp in Barcin-Höyük, Northwest Anatolia, near the Sea of Marmara. In France they were the Constructors of the large stone tombs, megaliths.
G2a2b2a1a1c1-Z724, in subgroups: N. Italy, Denmark, a tiny number of Ossetians and a Han Chinese from Beijing, and a group in Gao, Mali (Africa) problaby from Morocco. G2a2b2a1a1c1a-CTS4472. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1-CTS5990/Z1903 The earliest archaelogical find is from Chalcolithic Bulgaria around 6700 ybp, the TMRCA of all G-Z1903s today is at 4800 ybp. Now in Greece, Italy, Spain, Germany, France, Belgium, Netherlands, UK., Sardinians and in Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a-CTS7045, formed probably around 4500 ybp. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a1-L640 formed 4100 ybp, TMRCA 750 ybp, England, Ireland. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a1a-Y88/Z3520 formed 750 ybp, TMRCA 600 ybp, Great Britain. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a1a1-FGC348. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2-Z3428 formed 4100 ybp, TMRCA 4000 ybp. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2a-Z26414. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2a1-FGC7477/Z6523. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2a1a-Z27232. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2a1a1-Z6028 formed 3500 ybp, TMRCA 3500 ybp., Sierra Leone, in subgroups Lebanon, Great Britain, Morocco, Ukraine, Slovakia, Denmark, Polish, Moldavia, Deutschland. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1a2b-Z6032 formed 4000 ybp, TMRCA 4000 ybp, Sardinians, French, Sephardim, Ashkenazim and Araite jews, Christian Arabs from Syria and Lebanon, Berbers, Mende people from Sierra Leone, Ossetians, and a Han Chinese from Manchuria. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b-Z3428, Berbers. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1-Z26414, Berbers. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1a-FGC7477/Z6523, Sierra Leone, n.e. Europe (Ashkenazi Jews), Romania, U.K. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1a1-FGC249. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1a1a-FGC248/FGC263, Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1a1b-FGC31715, exist for abt 1,500 yrs, Ashkenazi Jews. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1a1a-FGC263. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1b-FGC23437, Europeans. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b1b1-Z22644. Austria. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b2a-Z6434. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b2a1-Z3571. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b2b-Z6033. G2a2b2a1a1c1a1b2c~Z43090. Italian and Irish. G2a2b2a1a1c1a2-Z40433, Scandinavians. G2a2b2a1a1c2-FGC12126 formed 9600 ybp, TMRCA 7900 ybp, formed, Han chinese (probably Hui origin) G2a2b2a1a1c2a-L660 formed 7900 ybp, TMRCA 3700 ybp, England, Poland (nobility), Slovakia. G2a2b2a1a1c2b-Z16670, formed 7900 ybp, TMRCA 1100 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G2a2b2a1a1c2b1-Z16713. formed 1100 ybp, TMRCA 850 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G2a2b2a1a1c2b2-Z31206formed 1100 ybp, TMRCA 600 ybp, Saudi Arabia. G2a2b2a1a1c3-PF4202, split drectly off from G-CTS342 so originated about 10,5 KY ago, Western Europe, Norwegians, France, Italy (M de P.) G2a2b2a1a1c3a~FGC37628. G2a2b2a1a1c3a1~FGC37658. G2a2b2a1a1c3a2~Z43844 Italy, Ireland. G2a2b2a1a1c3b~Z39539. G2a2b2a1a1c3c~PF790. G2a2b2a1a1d-S1415, Norwegians. G2a2b2a1a1e-Z30708, Middle Easterners, 11.000 years. G2a2b2a1a1f-Z39263. G2a2b2a1a1f~Z39264. G2a2b2a1a1g~Z39367. G2a2b2a1a1h~CTS8386. G2a2b2a1a1i~Z40367. * G2a2b2a1a2~Z38302, Y18491, formed 10.900 ybp, TMRCA 10900 yb,archaeological finds in the site Gurgy les Noisats (France), dated to the western European Neolithic around 68506500 ybp at 51 out of 57 male individuals and is the main male lineage of the group. The Paris Basin during the Middle Neolithic (around 47004300 BC) is well-known for the emergence of the monumental funerary architectural structures of the Passy phenomenon dedicated to select individuals from Neolithic communities. Gurgy les Noisats, a burial site in the Cerny cultural horizon without any monumental architecture, is located close to a dozen contemporaneous monumental sites.
* G2a2b2a1b-Z30527, 10.000 years. Ukrainians, Iraqi Jews. G2a2b2a1h-S1415, Iberians, 10.000 years. * G2a2b2a2-M278, Greeks, Spanish, present in the Medieval Jewish population of Spain in the 14th century. G2a2b2a3-Z6885, archaeological finds have been made in the Anatolian Neolithic from Barcin Höyük in Northwest Türkiye from c. 8300 BP (6500-6200 BCE) and the Linear Ceramic Culture - LBK - from Scheltz, Austria, 6950 BP (5500-4500 BCE.
G2a2b2a3a-Z39310. Archaeological find in a sample dated 7000 BP c. 5040-4850 cal BCE from the El Toro Cave in Antequera near Málaga, South Spain. This Andalusian Early Neolithic culture is thought to have arrived just prior to the Cardial technology.
G2a2b2a3a1-Z39308. G2a2b2a3a2-Z40745. G2a2b2a3b-Z6147. G2a2b2a3b1~ CTS7114. G2a2b2a3b2~ Z40218. G2a2b2a4-Z30503, formed 11.700, TMRCA 7400, Brahui, Kalash Punjabis and among Uyguhrs of Kazakhstan. G2a2b2a4a-Z40458. formed 7440 TMRCA, TMRCA 6600, Iraqis and Indians. G2a2b2a4a1-Z30522. Lyengar Brahmins and Bhargava in India. G2a2b2a4a2-Z40469. G2a2b2a4b-Z31387 Punjabi and Kalash. G2a2b2a5~ M426, Pakistan (Kalash). G2a2b2a6~ Z6030, Sardinian Italy. G2a2b2a7~ PF3912. G2a2b2a8~ L288.2. G2a2b2a9~ PF4685/Z2354. * G2a2b2b-PF3359, formed 14400 ybp, TMRCA 12400 ybp, was under the earliest Anatolian Aceramic Farmers of Boncuclu, is found in the following cultures: LBK, Iberia Late Neolithic, Varna Eneolithic, Iberia Chalcolithic, Nuraghic of Sardinia, a Hungarian Scythian of 392 BCE, a Viking Age Sweden from 870 CE, Musawi Sayyid from Iraq, Armenians, Southeastern Türkiye, and Southwest Iranians, Arabs, Crimean Tatars, a Kabardinian, a Moksha, a couple of Armenians, non-Ashkenazi Jews, a Central Greek, Cretans, Sardinians (here it is 25% of the G), Corsicans, a Hungarian, a German, a Brit, and in the Netherlands. G2a2b2b1-F1193, formed 12200 ybp, TMRCA 11800 ybp. G2a2b2b1a-PF3369. G2a2b2b1a1-F872, formed 11500 ybp, TMRCA 8900 ybp, Epipaleolithic Central Anatolia Boncuklu 10,200 ybp. G2a2b2b1a1a-PF3378, formed 8900 ybp, TMRCA 5800 ybp, Chaloclithic samples from Su Crocefissu Roma 5700 ybp and El Mirador Cave, Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain, 4850 ± 150 ybp, Hungary 2480 ± 40 ybp ; nowadays in Italia, Sardinia and Germany. G2a2b2b1a1a1-PF3420, PF3376, formed 5800 ybp, TMRCA 4800 ybp, Sweden in burial grounds in Sigtuna, 10 to 12th century. G2a2b2b1a1a1a-Z6035. G2a2b2b1a1a1a1-Z6452. G2a2b2b1a1a1b-Z46131. G2a2b2b1a1a1c-PF3409. G2a2b2b1a1a1d-PF6873. G2a2b2b1a1a2 Z7016, formed 5800 ybp, TMRCA 5200 ybp, Italia and Netherlands. G2a2b2b1a1a2a Z7022. G2a2b2b1a1b-PF3409. G2a2b2b1a1b1-PF3462. G2a2b2b1a1b2-PF3463. G2a2b2b1a1c-PF6873. G2a2b2b1a1b~-F2572, formed 8900 ybp, TMRCA 8600 yb. G2a2b2b1a1b1~F2686.2, UK. G2a2b2b1a1b1a F2214, formed 8600 ybp, TMRCA 8500 ybp. G2a2b2b1a1b1a1-M310.2, PF2402.2. G2a2b2b1a1b1a2 ~F807, formed 8500 ybp, TMRCA 2000 ybp, Netherlands. G2a2b2b1a2 FGC82036 G2a2b2b1b FGC52601 G2a2b2b1b1 Z46065 G2a2b2b1b2 A20535 G2a2b2b1b3 FGC52629 G2a2b2b1b3a FGC52664 G2a2b2b2-PH488, formed 12400 ybp, TMRCA 7400 ybp, Romania Early Neolithic, Armenia, Iran, Palestina.
G2a2b2b2a-CTS1455, PH236, formed 7900 ybp, TMRCA 3500 ybp, Poland. G2a2b2b2b~Z43316 G2a3b Former notation for what is now G2a2b2 * G2b-M3115, formed 21.000 ybp, TMRCA 20.000 ybp. G2b1-M377, formed 20.0900 ybp, TMRCA 8500 ybp, Lebanese; in subgroups is found in Lachin, Nagorno-Karabakh, in an Armenian noble family, in native Syrian Christians and their Lebanese Maronite descendants, in Italy, Sicily, Spain, Saudis of Khorasani origin, Kars Province Türkiye, as well as among Ashkenazi Jews and Pashtuns in Pakistan where it reaches till 14.7% in who claim Israelite ancestry and to be descended from a regular Jewish "Benjaminite" community in Khroasan (Eastern Greater Iran) who converted to Islam at the time of the Mongol Invasion in 1220 CE. G2b1a-Y12297, BY794, formed 8900 ybp, TMRCA 5200 ybp. G2b1a1-M283, M3124, formed 3800 ybp, TMRCA 1600 ybp, Italian. Pakistani, Afghans. G2b1a1a-FT360028, BY154721, G2b1a1b-M3146 , formed 1400 ybp, TMRCA 900 ybp, Pakistani, Afghans. G2b1a2-Y12976, FGC32402, formed 4,700 ybp, TMRCA 1050 ybp., Ashkenazim, Baltics and Austria.
G2b1a2a-Y15861/FGC35913, Ashkenazim. G2b1a2a1-FGC35915/Y15862/Z35608. Lithuanian Jewish and Belarus who are probably come from France. TMRCA of the parent 1100 ybp. G2b1a2a1a-Y67052. G2b1a2a2-Y16169/Z37831, formed 850 ybp, TMRCA 700 ybp, Israel. G2b1a2a2a-Z5999, BY21363.2, formed 700 ybp, TMRCA 600 ybp, Roumenia. G2b1a2a2b-Y81219, (BY165438?), formed 700 ybp, TMRCA 600 ybp. Ukraine G2b1a2a3-BY147680, . G2b1a2a4-BY37058,, G2b1a2b-Y14600, FGC32413, formed 1050 ybp, TMRCA 1050 ybp. G2b1a2b1-Y14601, FGC32409, formed 1100 ybp, TMRCA 850 ybp, Ukraine. G2b1a2b1a-FGC32397, formed 850 ybp, TMRCA 850 ybp, Germany, Latvia. G2b1a2b1b-FGC55702,formed 850 ybp, TMRCA 225 ybp, Poland. G2b1a2b2-Y50032, BY165834, Y52805 G2b1a2b2a-BY165834, G2b1a2b2b-BY181331 G2b1a3-CTS3357.2 * G2b1b2c-Z44684, Z44685, Z44686. G2b1b2d-Z45084, Z45086. G2b1b2e-Z45085, Z45086. G2b1b2f-BY197216. * G2b2-FGC3095, FGC3022, Italy, Armenians in Türkiye. G2b2a-FGC2916, Z8022, an archaeological find in the Zagros Mountains of Iran, 9,250 cal.BP. Nowadays in Syrians, Jordanians and Italians. G2b2a1-FGC2968, G2b2a2-Z45411, G2b2b-Y104063, Z37343, Armenians. G2b2b1-FT36625. G2b2b1a-FT37345. G2b2b1b-FT36417. *
| ||||